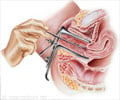
Treatment of Fibroids in Uterus
Fibroids do not require treatment in the absence of any symptoms. Patients may be re-evaluated periodically. Surgical scraping of the uterine cavity, i.e. dilation and curettage (D&C) is done for abnormal vaginal bleeding. Drugs may be used to relieve symptoms, reduce fibroid growth, or both.
Medications:
The following categories of drugs are resorted to:
- GnRH analogues: Gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists decrease oestrogen production by the body. As we have already seen, fibroids are supposed to grow in size under the influence of oestrogen. Thus GnRH analogues like Leuprolide and Goserelin thus help in shrinking fibroids. They are of great value when given before surgeries. Smaller size would mean easier surgery with little blood loss.
- Anti progestins: These are anti-hormonal drugs that reduce fibroid growth. Drugs like mifepristone are to be used with great caution.
- Exogenous progestins: Drugs like Medroxyprogesterone acetate or megestrol acetate can partially suppress estrogen stimulation of uterine fibroid growth
- Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs): Though drugs like raloxifene may help fibroid growth, their efficacy in reducing symptoms in comparison to other drugs is unclear.
- Danazol: This androgenic agonist is often less acceptable to patients because of the high rate of adverse effects. It can however suppress fibroid growth.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents, such as ibuprofen are used to treat pain.
Surgery:
Surgery is considered in the following situations:
- Rapidly evolving mass in the pelvis
- Repeated bleeding that does not respond to steroids.
- Persistent or intolerable pain or pressure
- Urinary or intestinal symptoms
- Infertility
- A history of recurrent abortions
Traditional surgical correction is Hysterectomy or myomectomy. Hysterectomy, i.e. surgical removal of the uterus is the definitive treatment. If women desire pregnancy or want to retain their uterus, myomectomy is done. Myomectomy is surgical removal of fibroids. Here fertility is retained. However recurrence of fibroids can happen.
Newer procedures:
- Laparoscopic and hysteroscopic myomectomy
- High-intensity focused sonography
- Cryotherapy: The use of extreme low temperatures
- Radiofrequency ablation: The technique uses high frequency alternating current
- Uterine artery embolization: This innovative modality involves clotting of the arterial blood supply to the fibroid. Once the blood supply to the fibroid is cut off it shrinks in size. This is a good option for women who do not want surgery or those who are not good candidates for surgery. Recovery is faster when compared to hysterectomy or myomectomy. Rates of complications are high though.
Choice of Treatment
Treatment strategy is individualised. Asymptomatic fibroids do not need treatment. Postmenopausal women are given a trial of expectant management since fibroids may regress in the absence of oestrogen. Surgically fit patients go through myomectomy (if pregnancy is desired). Inoperable ones require newer modalities like uterine artery embolization. If everything fails and conception is not desired hysterectomy is done (preceded by drug therapy).