- A.D.A.M Medical Encyclopedia
- Vesicular and bullous diseases. In: Habif TP, ed. Clinical Dermatology. 5th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Mosby Elsevier;2009;chap 16.
- Morelli JG. Vesiculobullous disorders. In: Kliegman RM, Behrman RE, Jenson HB, Stanton BF, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 18th ed. Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders Elsevier;2007:chap 653.
About
Epidermolysis bullosa (EB) is a group of inherited disorders in which the skin is extremely fragile. Skin blisters develop in response to minor injury. People with EB have an increased risk of cancers of the skin. Younger patients with the condition are often called “butterfly children” since their skin are said to be as brittle as a butterfly’s wings. Other descriptive terms used include “cotton wool babies” and “crystal skin children”.
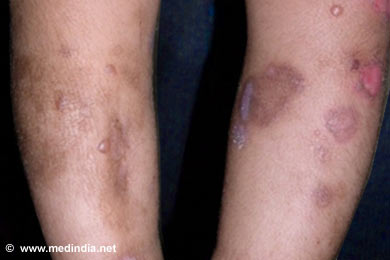
EB occurs in all racial and ethnic groups throughout the world and affects both sexes. About 50 babies in 1 million live births in the United States are diagnosed with EB. EB is usually diagnosed at birth or soon after. The condition may not be completely curable; treatment aims at the prevention of blister formation and related complications.
Causes, Incidence and Risk factors
The human skin has two layers: an outer epidermis and an inner dermis. The two layers are anchored together by protein anchors containing collagen. This prevents the two layers from moving independently of one another. People born with EB lack these skin anchors, and hence any action that creates friction between the layers generates blisters and painful sores. Rubbing the skin or applying pressure injures the skin.
Epidermolysis bullosa is of four main types:
- Dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa
- Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
- Hemidesmosomal epidermolysis bullosa
- Junctional epidermolysis bullosa
In addition to these, there are many subtypes. Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita is a rare type of EB, and is an autoimmune disorder. This type usually appears in adults over the age of fifty, although it occurs in children as well. It is linked to the inflammatory
Epidermolytic bullosa is a hereditary disease. Those with a family history of the disease are at an increased risk of developing EB.







