- Neurology and Neurosurgery - (http://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/neurology_neurosurgery/centers_clinics/peripheral_nerve/conditions/diabetic_neuropathy.html)
- Nerves (neuropathy) - (https://www.diabetes.org.uk/guide-to-diabetes/complications/nerves_neuropathy/)
- Diabetes and nerve damage - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000693.htm)
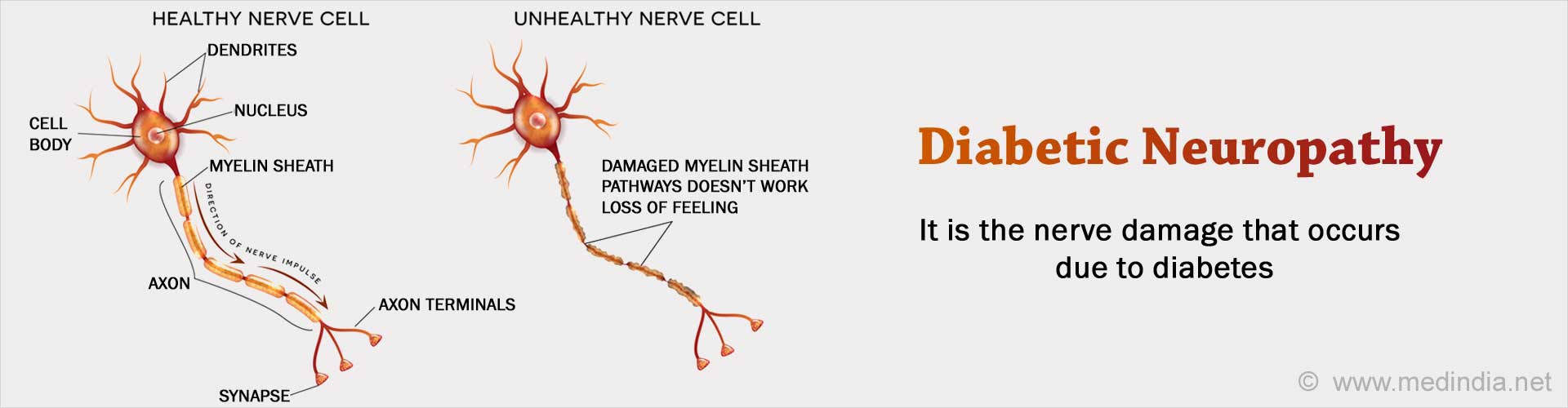
What is Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic Neuropathy is the nerve damage that occurs due to diabetes.
It is one of the complications in patients who have had diabetes for many years or in those with poor blood sugar control.
Diabetic neuropathy can affect nerves that:
- Bring and carry sensation in our body (sensory nerves)
- Cause movement(motor nerves)
- Are involved with involuntary functioning in the body like heart rate, breathing, digestion, urination and sexual desire (autonomic nerves).
Diabetes can affect the nerves arising from the brain (cranial nerves) or the spinal cord (spinal nerves).
Types of Diabetic Neuropathy
- Focal Neuropathy: In this type of neuropathy, only one group of nerves or a single nerve is affected causing pain in a localized area or weakness in the muscle supplied by the damaged nerve. Any nerve in the body can be affected.
- Proximal Neuropathy: This type of neuropathy causes pain and weakness in the thighs, hips and buttocks, thereby making it difficult to get up from a sitting to standing position.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Peripheral neuropathy is the most common type of diabetic neuropathy. Patients complain of numbness, tingling and pricking sensation in the feet, legs, hands and arms, increased sensitivity to pain or loss of balance or coordination. It can also cause muscle weakness if motor nerves are affected.
- Autonomic Neuropathy: Autonomic neuropathy is caused due to damage to the autonomic nerves which control digestion, bladder and bowel function, heart, blood vessels, lungs, sexual response and sweating. Damage to the autonomic nerves can cause fluctuations in blood pressure or heart rate, constipation, problems with digestion, loss of appetite, weight loss, leakage of urine (urinary incontinence), problems with sweating and impotence.
What Causes Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy can be caused due to combination of various factors such as:
- Presence of diabetes for many years
- High blood sugar levels
- High cholesterol levels
- Low insulin levels
- Damage to the blood vessels which supply the nerves. This results in inadequate supply of oxygen and nutrients to nerves and leads to nerve damage
- Autoimmune disease causing inflammation of the nerves
- Nerve damage tendency that runs in families (genetic)
- Nerve damage due to injuries and overuse
- Consuming alcohol and smoking

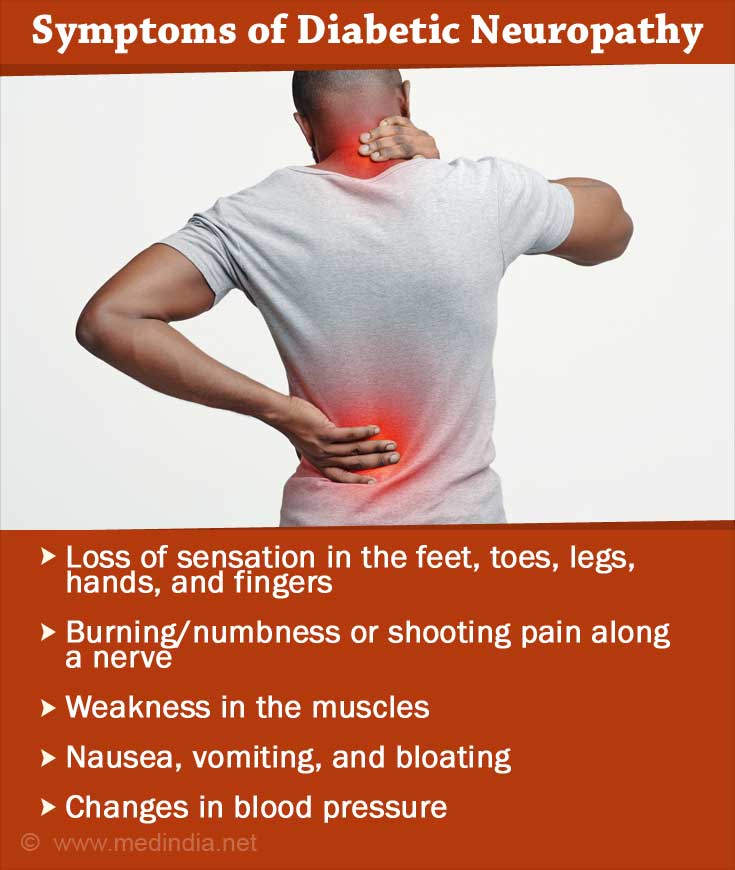
What are the Symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy?
Symptoms of diabetic neuropathy depend on the type of nerves that are affected.
Symptoms caused due to involvement of sensory nerves are:
- Loss of sensation, or pricking or tingling sensation in the feet, toes, legs, hands and fingers.
- Inability to detect changes in temperature
- Loss of coordination due to inability to detect joint position
- Loss of balance
- Burning or shooting pain along a nerve
Symptoms due to involvement of motor nerves include:
- Weakness in the muscles supplied by the affected nerve
- Thinning of affected muscles if left unused for prolonged duration. This is referred to as ‘wasting’ of muscle
Symptoms due to involvement of autonomic nerves include:
- Loose stools or constipation
- Nausea, vomiting, bloating due to slowed gastric emptying
- Leakage of urine (incontinence)
- Changes in blood pressure
- Giddiness (due to changes in blood pressure)
- Problems with sexual desire or sex in men and women
- Sweating too much
How to Diagnose Diabetic Neuropathy?
Diabetic neuropathy is diagnosed with general examination that includes assessment of muscle functioning, reflexes, response to touch, temperature and vibration. Blood pressure and heart rate are measured.
Foot examination is important in the diagnosis of diabetic neuropathy. The doctor might check for sensation of touch with a nylon filament or by pricking with a pin. Vibration sensation is best checked with a tuning fork.
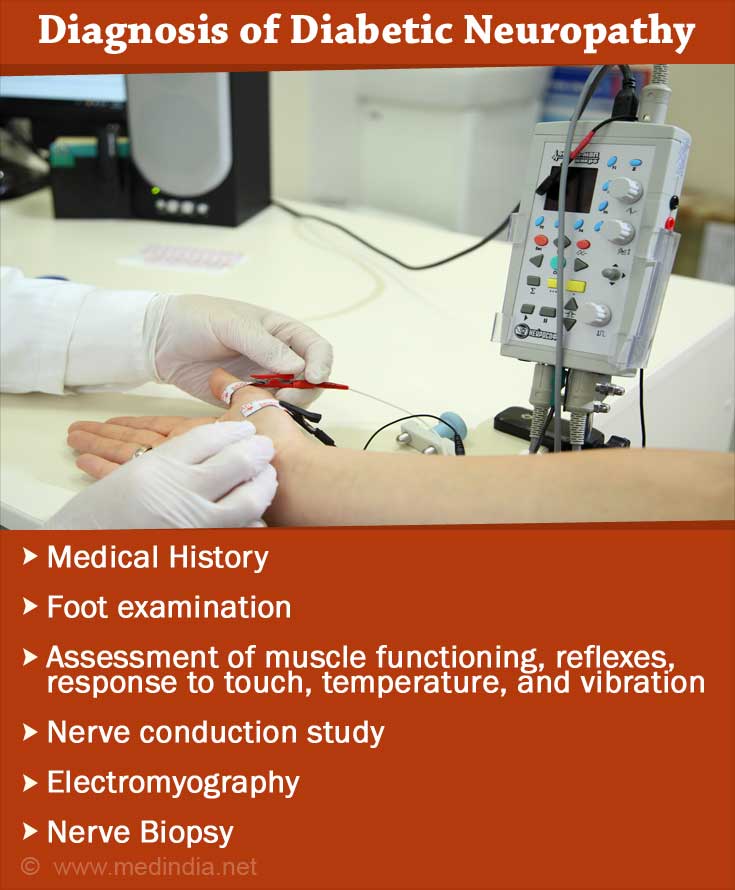
Other investigations like nerve conduction studies and electromyography are used to check the functioning of the nerves and muscles, respectively. A nerve biopsy may also be done if necessary.
What are the Complications of Diabetic Neuropathy?
Common complications of untreated or progressive diabetic neuropathy are:
- Charcot Joint: Charcot joint is a joint deformity that occurs in patients with diabetic neuropathy. It usually affects weight-bearing joints.
- Gangrene: Gangrene is the dead tissue that forms in an untreated wound due to diabetic neuropathy.
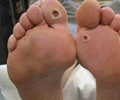
- Foot Ulcer: Foot ulcers develop in diabetic patients with neuropathy commonly because of loss of sensation in the feet. Loss of sensation in the feet does not cause any pain with minor injuries. This leads to formation of blisters or ulcers which are difficult to heal because of poor blood supply in diabetes patients.
- Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy: Damage to the nerves that control heart rate and
blood pressure causes dizziness upon standing due to drop in blood pressure in standing position (orthostatic hypotension). - Hypoglycemia Unawares: Normally, if the blood sugar drops, the patient experiences symptoms like palpitations and sweating that act as a warning sign to the patient. If the autonomic nerves are damaged, these symptoms may not occur and the patient is not aware of the low blood sugar levels. This is called ‘hypoglycemia unawares’.
What are the Treatments for Diabetic Neuropathy?
Treatment of diabetic neuropathy mainly depends upon bringing blood sugar levels under control. Pain due to diabetic neuropathy is best managed with tricyclic antidepressants, certain anticonvulsants, opioids, serotonin reuptake inhibitors and topical preparations like capsaicin and nitrate creams.
Other medications should be used depending on the symptoms of the patient.

In case of development of gangrene, removal of dead tissue is considered along with a course of
Diabetic patients are advised regular checkups, foot examinations and protective foot wear to prevent development of complications from diabetic neuropathy.
Prevention of Diabetic Neuropathy
Prevention of diabetic neuropathymainly depends upon avoiding the risk factors. This can be done by:
- Maintaining blood sugar levels close to normal range
- Getting enough physical exercise daily to maintain optimal body weight and to lower raised cholesterol levels.
- Limiting alcohol intake and quit smoking.
- Yearly check up to assess the functioning of the nervous system.
- Wearing good fitting footwear.
Health Tips
- Follow diet restrictions and exercise schedule to maintain blood pressure levels, weight and blood sugar levels.
- Limit alcohol intake and quit smoking.
- Consult your doctor if you feel any pain or numbness in your feet or toes.
- If you are diagnosed with neuropathy, it is important for you to take care of your feet and legs from injuries, which are usually not felt due to nerve damage.