Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is generally diagnosed with the help of blood tests and an intestinal biopsy. Blood tests are conducted to check for high levels of anti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies (tTGA) or anti-endomysium antibodies (EMA).
Celiac disease poses a challenge for diagnosis due to its similarity with symptoms of other diseases like Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Iron-deficiency anemia and intestinal infections. Celiac disease is generally diagnosed with the help of blood tests and an intestinal biopsy.
If you have a clinically diagnosed irritable bowel disease or an inflammatory bowel disease, it is possible that the underlying cause maybe celiac disease. Mis-diagnosis is common as the symptoms of all these conditions overlap. The treatment of the conditions are different, but at least if celiac disease is confirmed one can make adjustments in the diet and be symptom free.
In one of the studies, 145 patients with irritable bowel syndrome, 74 patients with celiac disease and 57 patients with ulcerative colitis were given gluten free diet and also assessed by blood markers. Success was achieved in both those who had positive markers and also in those where the markers were negative.
Blood Test
One of the best ways to diagnose Celiac Disease is to check for levels of certain auto antibodies in the blood. Generally, people with celiac disease carry abnormally high levels of auto antibodies, proteins which attach the body’s own cells and tissues in the blood. Blood tests are conducted to check for high levels ofanti-tissue transglutaminase antibodies (tTGA)or anti-endomysium antibodies (EMA).
Those who do not exhibit any symptoms of Celiac Disease should be screened for the presence of auto antibodies in the blood. It is also advisable for those with a family history of Celiac Disease to undergo screening to check the presence of the disease.
For accurate results, it is advised that patients should eat a diet with gluten, like bread and pastas, before the blood test.
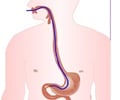
Intestinal Biopsy
If the symptoms and blood tests point towards Celiac Disease, then a biopsy of the small intestine is conducted to confirm the diagnosis.
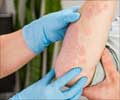
Skin biopsy and blood tests are conducted to diagnose Dermatitis Herpetiformis.If the skin biopsy reveals the characteristics of DH and if antibody tests turn positive, the diagnosis is confirmed. In such cases, patients need not undergo an intestinal biopsy.
There is a connection between celiac disease and other immune disorders of the body and this connection maybe genetic. It is advisable in this situation to rule out celiac disease if there are gastro-intestinal symptoms. Some of these autoimmune conditions include -
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Type 1 diabetes
- Thyroiditis (autoimmune)
- Asthma
- Eczema
- Addison’s disease
- Sjögren’s syndrome – causing dryness of eyes and salivary glands.
A number of “psychiatric” disorders such as - depression, anxiety and epilepsy maybe associated with gluten intolerance and in such situations screening for celiac disease may need to be undertaken.