- Neuroanatomy, Cranial Nerve 8 (Vestibulocochlear) - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk537359/)
- The Human Auditory Brainstem Response to High Click Rates - (https://pubs.asha.org/doi/10.1044/1059-0889(2001/008))
- Auditory Brainstem Response Wave Amplitude Characteristics as a Diagnostic Tool in Children with Speech Delay with Unknown Causes - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4967486/)
- BAER - brainstem auditory evoked response - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003926.htm)
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear - (https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=90&contentid=p02025)
- Hearing Loss - An Overview - (https://www.american-hearing.org/disease/hearing-loss-an-overview/)
- Perceptual Encoding in Auditory Brainstem Responses: Effects of Stimulus Frequency - (https://pubs.asha.org/doi/10.1044/2018_JSLHR-H-17-0486)
- Auditory brainstem response - Wikipedia - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/auditory_brainstem_response)
- Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test - (https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/abr-test.html)
- The Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response in Old Versus Young Horses - (https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/817d/66e48971de5148bcafc46a989ba6ec7bfce0.pdf)
What is Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry (BERA)?
Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry (BERA) is an objective test to understand the transmission of electrical waves from the VIIIth cranial nerve to the brainstem, in response to click sounds given through the ear.(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
BAER - Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response
Go to source) The procedure is also called Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR), Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potential (BAEP), Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response (BAER) and Evoked Response Audiometry (ERA).(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
The Human Auditory Brainstem Response to High Click Rates
Go to source)
Brainstem Evoked Response was first described by Jewett and Williston in 1971. The test procedure and the interpretation of the results are typically done by an audiologist.(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Auditory Brainstem Response Wave Amplitude Characteristics as a Diagnostic Tool in Children with Speech Delay with Unknown Causes
Go to source)
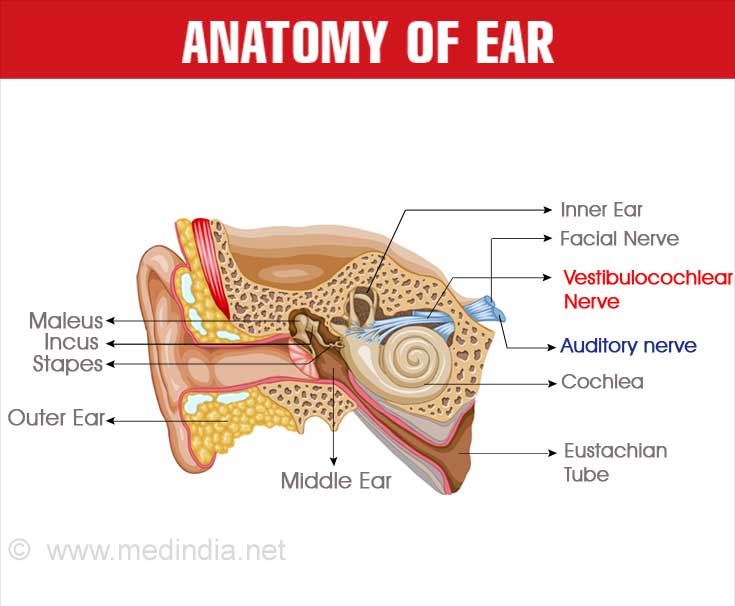
When a sound reaches the ear, it passes through the external ear canal and vibrates the eardrum. These vibrations are conducted by three small bones in the middle ear, the malleus, incus and stapes to the inner ear.(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear
Go to source) The inner ear contains the cochlea, which plays an important role in hearing, and the vestibular part, which is involved in maintaining balance. Signals for hearing and balance from the inner ear are carried by the 8th cranial nerve, also called the vestibulocochlear nerve, to a vital part of the brain called the brainstem.(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Neuroanatomy, Cranial Nerve 8 (Vestibulocochlear)
Go to source) Signals then pass on to the part of the brain where they are interpreted.
BERA is generally used to identify any pathology in the vestibulocochlear nerve or the brainstem. The test is recommended for infants who are at a high risk for hearing loss and in whom conventional audiometry cannot be performed.(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hearing Loss - An Overview
Go to source)
How is Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry Performed?
The following are the steps involved in the procedure of Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry:
- The person is made to lie back on a reclining chair or on a bed and is asked to remain still. For infants, it is usually done when they are sleeping.
- Stimulus is given in the form of a click sound or tone pip, via an ear phone or head phone. The stimulus is of varying loudness and of the frequency range from 1000 to 4000 Hz.(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Perceptual Encoding in Auditory Brainstem Responses: Effects of Stimulus Frequency
Go to source)

- The waveforms of impulses are produced at the brainstem in response to the sound stimulus.
- These waveforms are recorded by the electrodes that are placed over the scalp at various places as follows:
- Non-inverting electrode over the vertex of the head, which is the most prominent point at the back of the head
- Inverting electrodes on each ear lobe or mastoid prominence, the hard bony prominence behind each ear
- Earthing electrode over the forehead.
- The generated waveforms are amplified through various electrical procedures easy recording of waveforms.
- The peaks of the waveform are labeled as Wave I to Wave VII.
- The time interval between the waveform and the click stimulus is usually within 10 milliseconds.
- Various readings in different positions and polarities are recorded and marked.
- The recorded waves are sent for interpretation.
Preparing for Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry Test(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Test
Go to source)
- The hair must be oil-free. The person undergoing the test is advised a shampoo bath before the testing procedure.
- Lying still is very important for the BERA procedure. So, a mild sedative may be administered to the person or infant to sleep during the procedure.
What are the Indications of Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry Test?(9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Auditory Brainstem Response - Wikipedia
Go to source)
BERA procedure is recommended:
- To identify the site of the hearing problem. The test detects pathologies from the vestibulocochlear nerve up to the brainstem.
- As a hearing screening test in hyperactive, intellectually impaired or other children who would not able to respond to conventional audiometry.
- Asymmetric hearing loss - hearing loss that is more in one ear than the other.

- As a hearing screening for infants who are at high risk of hearing impairment like:
- Family history of congenital hearing loss
- Hyperbilirubinemia or high bilirubin levels
- Deformities or malformations of the head and face
- Head Injury
- Parental concerns about hearing levels in the child
- Nervous system abnormalities and suspected acoustic neuroma, which is a benign tumor of the 8th cranial nerve.
Results of Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry Test
The auditory evoked potential signals produced by the brainstem are recorded as waves containing peaks and troughs. The peaks are positive potentials that are recorded from the electrode at the vertex and are marked as wave I, wave II and so on up to wave VII.(10✔ ✔Trusted Source
The Brainstem Auditory Evoked Response in Old Versus Young Horses
Go to source)
The waves I to VII are believed to arise from parts of the brainstem which are listed below:
- Cochlear nerves – Wave I and Wave II
- Cochlear nucleus (Brainstem) – Wave III
- Superior olivary complex – Wave IV
- Lateral lemniscus – Wave V
- Inferior colliculus (Midbrain) – Waves VI and VII
In normal hearing adults, the response to the click stimulus presented for about 1 to 10 milliseconds is recorded. Responses beyond 10 milliseconds are thought to be potentials that arise from thalamus (10-80ms) and cortex (80-500ms) of the brain.
The following parameters are measured:
- Amplitude of the wave – indicative of the number of neurons firing
- Latency – speed of transmission
- Time interval between peaks
- The difference in wave V latency of one ear compared to the other.
Applications of Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry Test
BERA is an effective tool that can be used for various screening, testing and surgical monitoring procedures:
- Hearing aid selection and fitting in infants and children.
- Development and surgical fitting of cochlear implants.
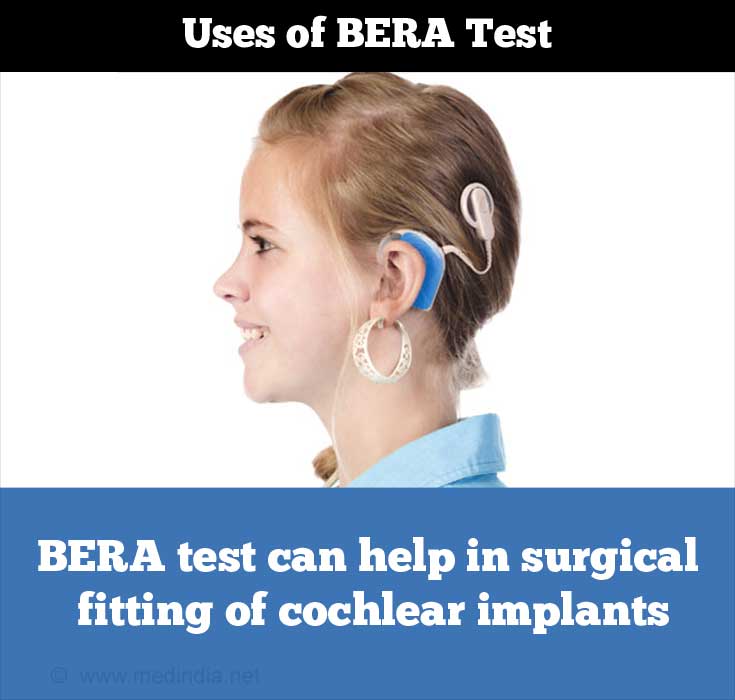
- Evaluation of hearing loss due to retro-cochlear pathology (lesion beyond the cochlea), like acoustic neuroma or acoustic schwannoma.
- Screening for hearing loss in newborns, infants and other young children.
- Diagnosis of any suspected demyelinated disorders like multiple sclerosis.
- Monitoring of central and peripheral nervous system during surgical procedures like treatment of facial palsy or Mèniére’s disease
Risks Associated with Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry Test
There are no known risks of undergoing Brainstem Evoked Response Audiometry.
The interpretation of the results however, has to be done carefully. This is because the recordings of the electric potentials generated by the neurons can be contaminated by the potentials generated by the muscles where the electrodes are placed.