- Treatment of Blood Clots - (http://circ.ahajournals.org/content/106/20/e138.full)
- Blood Clots and Strokes: A Guide for Parents and Little Folks - By Maureen Andrew, Maureen Andrew, MD.
- Blood Clotting Disorders (Hypercoagulable States) - (http://my.clevelandclinic.org/heart/disorders/vascular/hypercoagstate.aspx)
About
What is a Blood Clot?
An abnormal blood clot forms when there is damage to the lining of an artery or stagnation of blood in a vein, it obstructs the normal circulation of blood.
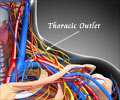
Blood constantly circulates in blood vessels. The heart pumps oxygen-rich blood, which reaches the different parts of the body through the arteries. It receives oxygen-poor blood from all parts of the body through veins, which it redirects to the lungs to get oxygenated.
Blood contains different types of cells such as red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, in addition to clotting factors and other proteins.
Clotting of blood is a natural defense mechanism of the body in response to an injury or cut to prevent excessive blood loss. The platelets initially form a plug over the bleeding site, which is reinforced by a mesh formed by the clotting factors.
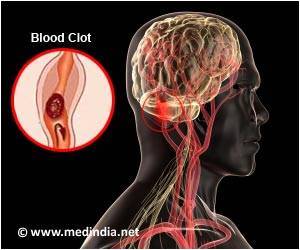
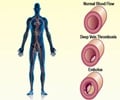
Sometimes, a clot can form even in the absence of a cut. This often happens when there is damage to the inner lining of the blood vessel or if there is stagnation of blood in a particular part. Some people have genetic or other factors that predispose them to developing blood clots. Clots that form inside large veins result in a condition called deep vein thrombosis. Parts of the clot may break and travel to other organs, resulting in embolism. If the embolus gets lodged in the lungs, the condition is called pulmonary embolism. Sometimes, the clots form in arteries as well.
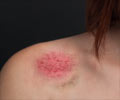
Signs and symptoms of a blood clot are based on the location of the clot. Arterial clots can cause angina, heart attack, stroke, peripheral arterial disease as well as bloody diarrhea. Venous clots often cause swelling, warmth, redness and pain in the affected limb.
Diagnosis is based on patient history, physical examination and diagnostic tests like blood tests, chest X-ray, electrocardiogram, CT-scan and fluoroscopy. Superficial clots are treated symptomatically with warm compresses and mild medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen. Deep venous and arterial clots are treated using blood thinners or drugs to break the clots.