- Amnesia - An Overview - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Amnesia#Types)
Types of Amnesia
There are six different types of
a) Anterograde amnesia
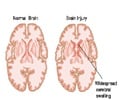
Anterograde amnesia happens as a result of brain trauma that involves the hippocampus, fornix, or mammillary bodies.
Here the patient is unable to recollect events, that occur after the onset of the amnesia, for more than a few minutes. In other words, in these patients, recent events are not transferred to long-term memory. For example the patient is unable to recollect what his colleague’s name is or what he had for breakfast or which movie he saw the day before.
Although the person's intelligence, personality and judgment are intact he may have trouble in retaining his job because his day- to- day functional memory is poor. This can be devastating to the person and to his family. However, with the use of memory aids the affected person can, more or less, lead a useful life.
b) Retrograde amnesia
In this form of amnesia the affected individual will be unable to recollect events that occurred before the amnesia set in. The condition is caused either by disease or a brain injury especially in areas linked with episodic memory—the hippocampus and the median temporal lobes.
Memory is poorest regarding events that occurred just before amnesia set in. Early memories are comparatively safe with memory decline building up to the event. No cure has yet been found for this condition.

c) Dissociative amnesia
Dissociative amnesia is a condition in which the patient is unable to remember vital personal information in a way that has nothing to do with normal forgetfulness. It is commonly seen in individuals who have witnessed a violent crime or a grave accident and does not occur due to a medical illness.
Patients with dissociative amnesia do not experience an identity crisis but they tend to pass through a trance-like state and may develop depersonalization as an effort to block out a stressful experience. Subtypes include –
- Generalized amnesia- When the amnesia involves the person’s whole life.
- Localized amnesia - no memory of a specific traumatic event that took place
- Selective amnesia- remembers only selective parts of events that occurred in a defined period of time.
- Systematized amnesia – memory loss regarding a specific category of information.
d) Infantile amnesia
The inability to recall events from early childhood is known as infantile amnesia. It is assumed that this happens due to immaturity in certain areas of the brain in the very early stages. Today, this state is seen as an intricate part of human development as it is now clear that memories begin to form only when certain parts of the brain are well formed.
e) Transient Global Amnesia (TGA)
In this type of amnesia there is temporary impairment in an otherwise healthy person's memory.
During this period of amnesia, the person is unable to recall recent occurrences, visuals or verbal information for more than a couple of minutes. Patients retain their identities, immediate recall abilities, distant memories, attention span, language function, visual-spatial and social skills.
However, they are often very confused by the ambience and the people around them. Although the period of memory loss does not usually last for more than a day the experience can be frightening! Some of the victims experience headache, dizziness, and nausea along with memory loss. Once recovered, the individuals are able to remember what occurred during the period of memory loss.
TGA generally affects fifty to eighty-year-old men. Its incidence is 3.4 to 5.2 people per 100,000 per year and the condition mostly affects 50-80 year olds.
Causes of TGA remain controversial. They include -
- Emotional stress
- Strenuous physical exertion
- Transient ischemic attack, a "mini-stroke."
- Basilar artery migraine,
f) Wernike-Korsakoff's psychosis –
This amnesia is a progressive disorder caused by extended alcohol abuse. It is usually accompanied by neurological dysfunctions such as loss of co-ordination during movement or a feeling of numbness in the fingers and toes.(2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Amnesia - An Overview
Go to source)