Glossary
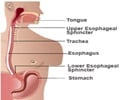
Esophagus: The muscular tube through which food passes from the throat to the stomach.Sphincter: A circular band of muscle fibers that constricts or closes a passage or opening
Enzymes: A protein that speeds up chemical reactions in the body.
Asthma: Disease with recurrent attacks of breathing difficulty characterized by wheezing. It is caused by spasms of the bronchial tubes, which can be caused by many factors including adverse reactions to drugs, vitamins, minerals or medicinal herbs.
Larynx: The area of the throat containing the vocal cords and used for breathing, swallowing, and talking. Also called the voice box.
Endoscopy: The use of a thin, lighted tube (called an endoscope) to examine the inside of the body.
Cancer: A term for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control. Cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and can spread through the bloodstream and lymphatic system to other parts of the body.
Angina: Chest pain, with sensation of impending death. Pain may radiate into jaw, ear lobes, between shoulder blades or down shoulder and arm on either side, most frequently the left side. Pain is caused by a temporary reduction in the amount of oxygen to the heart muscle through narrowed, diseased coronary arteries.
Gastritis: Inflammation of the lining of the stomach.
Laparoscopy: The insertion of a thin, lighted tube (called a laparoscope) through the abdominal wall to inspect the inside of the abdomen and remove tissue samples.
Antacids: Neutralizes acid. In medical terms, the neutralized acid is located in the stomach, oesophagus or first part of the duodenum.
Histamine: A chemical released in the body during an allergic reaction, causing inflammation; also used in medical treatment, especially to dilate capillaries.