- Intussusception - (http://kidshealth.org/en/parents/intussusception.html#)
- What is intussusception? - (https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?contenttypeid=90&contentid=p02002)
- Intussusception - children - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000958.htm)
What is Intussusception?
In intussusception, usually a part of the small intestine invaginates (folds into) into another section of intestine. It is like part of a collapsible tubular telescope of a camera that retract into one another. Intussusception is a medical emergency as it can often cause acute obstruction due to the swelling and inflammation of the intestines.
The leading part that invaginates into the other is called the intussusceptum, and the part that receives the leading part of the intestine is called the intussuscepiens.
Intussusception can occur in both children and adults, but it is more common in infants above 5 months of age and below one year. Also, boys are more commonly affected in comparison to girls.
The exact cause for intussusception is not known. In the pediatric population 90 % of the cases the cause is unknown (or Idiopathic - a spontaneously occurring condition for which the cause is unknown). However, in some cases, it is thought to happen due to viral infections, tumor or polyps in the intestine.
Intestinal developmental defects present at birth increase the chances of developing intussusception.
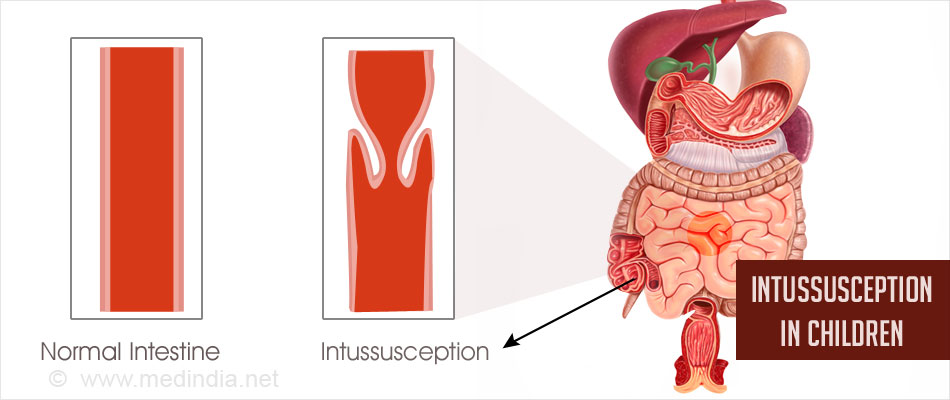
The most common site for intussusception is the area where small intestine meets the large intestine (ileo-colic region). Specifically it occurs because the ileum invaginates into the cecum through the ileo-cecal valve.
With intussusception, blood supply to the affected part of the intestine is reduced or disrupted. This leads to swelling in that area and intestinal obstruction. This reduction in blood supply can lead to chances of tissue necrosis, bleeding or rupture of the intestine. This in turn can cause infection in the abdominal cavity and lead to sepsis and shock.
Intussusception is a medical emergency and requires immediate medical assistance to prevent major complications like gangrene (death of intestinal tissue with infection) of the intestine, peritonitis, sepsis and shock.
Usually, if treatment is taken up within 24 hours or even sooner the chances of developing complication is less.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Intussusception in a Child?
Symptoms of Intussusception in a Child:
- Sudden severe colicky abdominal pain alternating with periods of no pain
- As the condition progresses, further pain only more pronounced and intense. The baby pulls up the knees to the chest during episodes of such pain and cries out loud
- Vomiting with bile
- Blood and mucus in the stools - the stools are described as “currant jelly” stools
- Lethargy
Signs of Intussusception in a Child:
- Swelling in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen
- Fever
- Dehydration

What are the Complications related to Intussusception in a Child?
- Gangrene due to Necrosis and infection of the associated intestinal tissue
Severe bleeding in the abdomen - Peritonitis - inflammation of the peritoneum (the membrane lining the abdominal cavity)
- Sepsis
- Shock (cold, clammy skin with a weak and rapid pulse)
What is the Incidence of Intussusception?
- The mean incidence of intussusception was 74 per 100,000 among children, 1 year of age.
- Peak incidences is usually between 5 and 7 months
- (Incidence of intussusception is from 82 studies that were analyzed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, USA. The National Institute of Hygiene and Epidemiology, Vietnam and the University of Melbourne, Australia and published in PLOS in 2013.)
- Fatal cases were higher in Africa (9%) compared to other regions (1%).
- A study published in 2014 in the Journal of Pediatrics quotes that the rate of intussusception among children greater than 15 weeks is substantially higher in Vietnam than in other parts of the world..
- Intussusception peaks seasonally that coincides with viral gastroenteritis in some populations
- Only 30% of intussusception cases are reported in children over 2 years of age.
What are the Risk Factors for getting Intussusception in Children?
- Age - occurs mostly in infants between 5 months to one year
- Gender - Boys are more affected than girls
- Intestinal Malrotation where the intestine does not rotate properly
- Having had an intussusception once makes the child more prone to a recurrence of the intussusceptions
- There maybe a genetic factor based on anatomical factors of development of the intestines
What are the Causes of Intussusception in Children?
Among children, 90% of the intussusception cases are idiopathic. In other words, it is a spontaneously occurring condition with no known cause.
However, in some cases the following factors might be the cause:
- A “lead point” or an underlying cause like a polyp or a benign tumor like a fat tissue lipoma.
- Meckel's diverticulum, a congenital bulge or an abnormality in the small intestine
- Intestinal Mal-rotation like in a condition called Waugh's syndrome
- Anatomical features of the gastrointestinal tract
- Hypertrophy or enlargement of Peyer’s patches (lymphoid tissues in the walls of the small intestine) and lymph nodes.
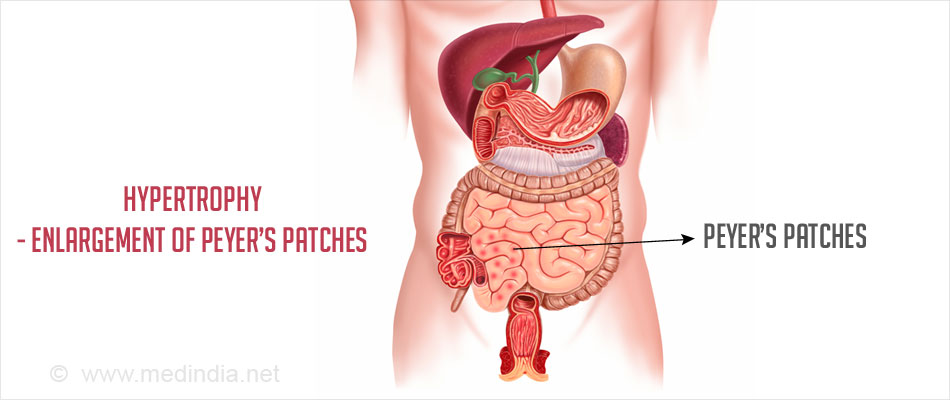
The enlargement could be caused due to infections by Adenovirus and Rotavirus and by non-infectious factors like intestinal allergies, celiac sprue, and Crohn’s disease.
What is the Diagnosis of Intussusception in Children?
Intussusception in a child is diagnosed based on the symptoms described by the parents like severe abdominal pain, bilious vomiting, stools with blood, mucus and radiographic investigations.
Quick non-invasive, cost-effective diagnostic methods are used to treat intussusception in children as the causes are mostly idiopathic.
Common tests done to confirm the presence of intussusception in children include:
- Abdominal X-ray - This is the first and basic investigation that is performed routinely. It might show multiple fluid levels with dilated proximal segment filled with gas. It might not be useful in the early stages of intussusception for confirmation of diagnosis.
- Bowel Enema - This may serve both as investigation and treatment for intussuception. Two types of enema are used - namely air and barium enema. Barium enema serves as the gold standard method (crescent sign) for diagnosing intussusception. The enema may itself reduce the intussusception and therefore serve as treatment for the condition.
- CT / MRI Abdomen - These tests are used more often for diagnosing intussusception in adults than in children.
- Serum Electrolytes - Serum electrolytes are useful in assessing dehydration.
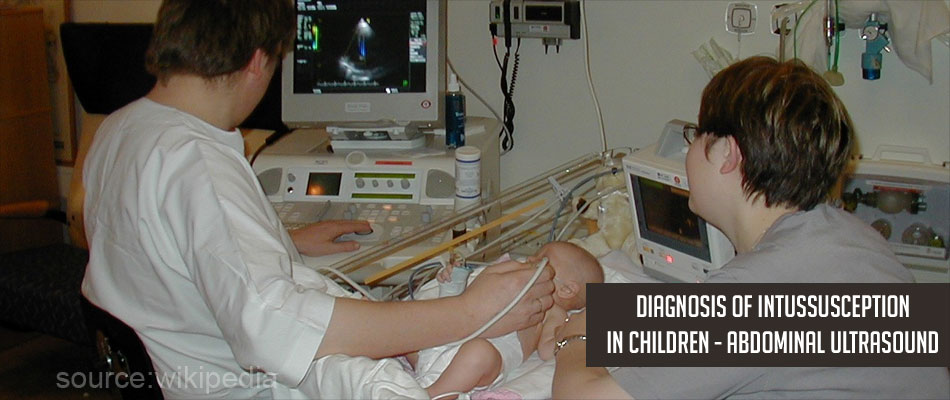
- Abdominal Ultrasound - This is the investigation of choice as it is very effective in concluding the diagnosis. A target, doughnut or a bull’s eye sign on the transverse view is the classical finding in case of intussusception.
What is the Treatment for Intussusception in Children?
A. Conservative
- Initial treatment includes management of dehydration due to vomiting with intravenous fluids such as normal saline.
- A tube is put through the child's nose and into the stomach (nasogastric tube) to decompress the intestines
- Conservative methods like air or bowel enema can be employed for treating bowel intussusception and reducing the obstruction without rupture of bowel.
- Barium (liquid mixture) is passed through a soft, tube placed into the rectum of the baby / child. This reveals the presence of the intussusception when the bowels are viewed through an X-ray. The pressure produced by barium unfolds the bowel and clears the blockage.
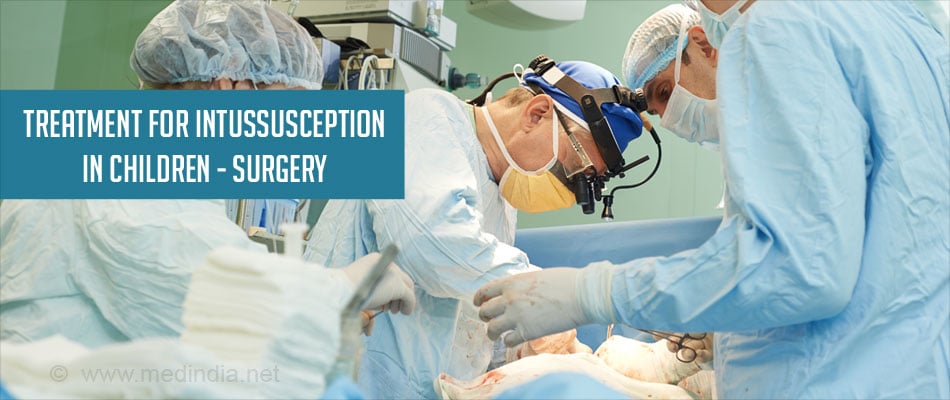
- In case of rupture of bowel, peritonitis, sepsis or shock and failed treatment with enema, surgical intervention becomes an emergency.
B. Surgical Approach
- In case the enema fails to reduce the intussusception surgery is undertaken with an incision into the belly under anesthesia to save the affected part of the bowel.
- In case of death of tissue (affected bowel), surgical removal of the affected segment of intestine is considered. The two parts of the healthy intestine are sewn back together to keep the continuity.
- In extreme cases, the damaged intestinal portion might be so large that surgery cannot link the healthy parts together.
“Ileostomy” is done in case of complications such as gangrene, sepsis or peritonitis and it can be a life-saving procedure for a sick child. In ileostomy a healthy intestinal end is brought out on the abdominal surface. The digested food in the form of stool passes out through this and gets collected in a bag that is fitted to the abdomen. This procedure is usually temporary.
The intravenous fluids continue till the normal bowel functions returns. The doctors monitor the child to make sure the intussusception does not return. Antibiotics may be given to prevent infection.
How should you Treat Recurrent Intussusceptions?
Intussusceptions return within 72 hours in 1 out of 10 kids who have undergone barium enema treatment.
Probability of recurrence of intussusception was 100% after the fourth episode. Therefore surgical intervention is a must after the third episode of intussusception.
What is the Prognosis for Intussusception in Children?
Prognosis or outcome is good with early treatment. In case of complications, it could be fatal in infants and young children if not treated immediately.







