- What is Fat? - (https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/fat)
- Interesterified fat - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/interesterified_fat)
- Fats and oils - (https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/fats-and-oils)
- Monounsaturated Fats - (http://www.heart.org/heartorg/healthyliving/healthyeating/nutrition/monounsaturated-fats_ucm_301460_article.jsp#.v-pquu_u_iu)
- Fat - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/fat)
- Dietary fats explained - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/patientinstructions/000104.htm)
- Choosing Healthy Fats - (http://www.helpguide.org/articles/healthy-eating/choosing-healthy-fats.htm)
- What Is Cholesterol? - (http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/hbc)
- Omega-3 fatty acids as treatments for mental illness: which disorder and which fatty acid? - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc2071911/)
Health Benefits of MUFA and PUFA
Know your monounsaturated fatty acids & polyunsaturated fatty acids. All that you wanted to know about MUFA & PUFA, recommendation, ratio and foods list.
All about Fat
One of the three macronutrients is fat, with carbohydrate and protein being the other two. They are esters comprising three fatty acid chains and the alcohol glycerol. They resemble capital E shape with the glycerol as the "backbone". Fats are also called triglycerides. Fat contains 9 calories per gram, unlike carbohydrates and protein, which each, have 4 calories per gram. Most fats that are found in food are made up of medium to long-chain fatty acids.
Importance of Fat in Human Body
Fat plays an important function in human body. Some of the key functions are mentioned below.
Provides Energy
Though the prime source of energy in human body is carbohydrates, fat is used as a source of backup energy when carbohydrates are not available. Unlike carbohydrates and protein one gram of fat has 9 calories. Excess calories are stored as lipids in adipose cells. During rest and even for daily activities, the body uses these lipids as fuels. Stored fat serves as fuel for subsequent use.
Vitamin Absorption
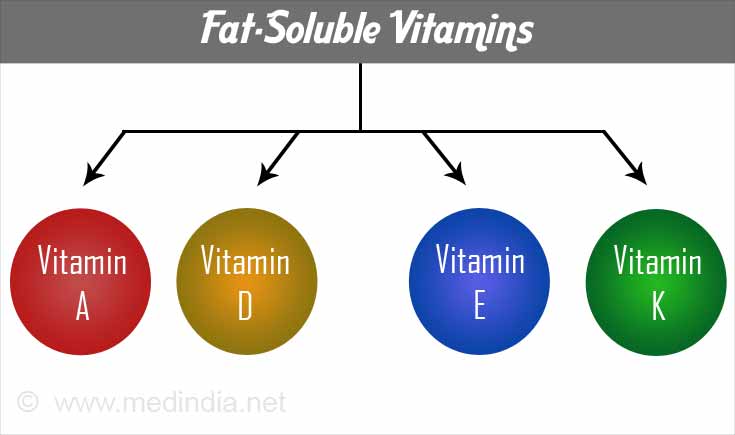
Some types of vitamins depend on fat for absorption and storage. Vitamins A, D, E and K, are fat-soluble vitamins and require adequate daily fat intake in order to function. These vitamins maintain the health of our vision, bones, teeth, skin, and blood.
Insulation
Fat cells are stored in adipose tissue and it helps to insulate our body and maintain a normal core body temperature. If the skin temperatures fall significantly, fat deposits are used to release heat. Fat works as insulator and keeps the heat inside.
Protection of organs
Major organs including the brain; nerves, tissues and bones are surrounded with fat. Fat provides protective cushion or buffer; against sudden impact or severe trauma and acts as shock-absorber.
Hormone Production
Cholesterol is a lipid that produces important steroid hormones in our body. Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and the active form of vitamin D are all formed from cholesterol which is needed to maintain pregnancy, regulate calcium levels in the body and develop sex characteristics.
Cell Wall Structure
The essential lipids, linolenic acid and linoleic acid, cannot be made in human body and is consumed from our diet. They help in the production of cell membranes and hormones, and provide structure and support to the cell walls in our body. Communication between cells is also dependent upon lipids. Fat helps to control the movement of substances in and out of the cells.
Healthy Brain
Fat creates the structural components for fatty insulating sheath called myelin. Myelin surrounds the various nerve fibers that are responsible for carrying messages efficiently.
What are the Recommended intakes of Fat in the Diet?
The National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) recommends an eating pattern which is lower in saturated fat and cholesterol. The optimal fat intake for children is unknown; however, 30 percent of calories from fat seems sensible for adequate growth and development.
- Less than 7 percent of calories from saturated fat.
- An average of 30 percent of calories or less from total fat.
- Less than 200 mg a day of dietary cholesterol.
Other recommendations include:
- 10 percent or less of total calories from polyunsaturated fat intake
- 15 to 20 percent of total calories from monounsaturated fat
- Ratio of omega 6: omega 3 fats is 5:1.
What is Monounsaturated Fats?
Monounsaturated fats or MUFA are fat molecules with one double bond in the fatty acid chain and the remaining carbon atoms are single-bonded. Oils with MUFA are liquids at room temperature and semisolid or solid when chilled. Sources of MUFA are natural foods such as whole milk products, nuts, red meat, and high-fat fruits such as olives and avocados. Sunflower oil contains as much as 85% MUFA while olive oil is about 75% MUFA. Cashews and canola oil contain about 58% monounsaturated fats. Tallow (fat from beef or mutton) and lard have less than 50% MUFA. Oils of almond, corn, sesame, peanut, grapeseed, safflower, avocado and whole grain wheat are other sources of MUFA.

What is Polyunsaturated Fats?
Polyunsaturated fats or PUFA are lipids which has two or more carbon–carbon double bonds. Oils containing polyunsaturated fats are generally liquid at room temperature and turn solid when chilled. Fatty acid viscosity and the melting temperature, increases in inverse proportion to double bonds. MUFA has higher melting point than PUFA as the later has more double bonds.
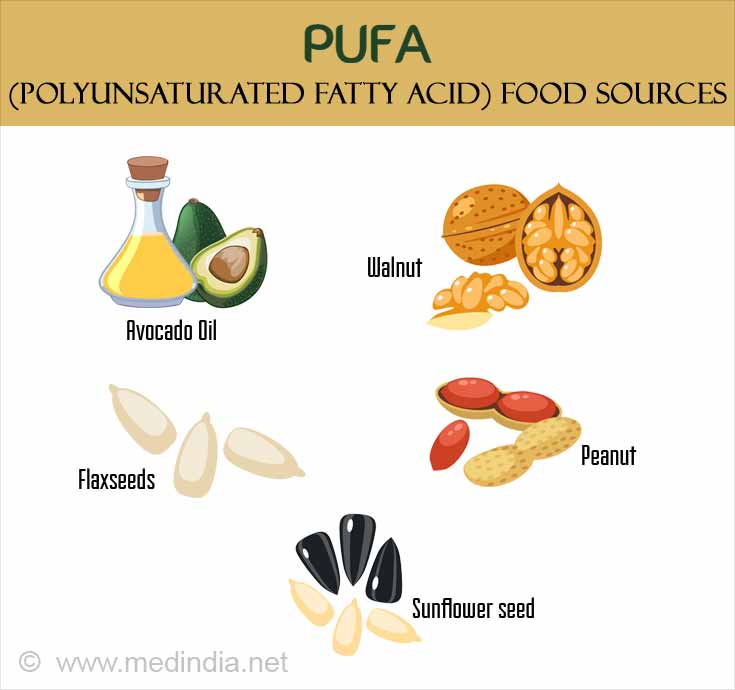
Sources of PUFA include walnuts, sunflower seeds, sesame seeds, peanut butter and peanuts, flaxseed, poppy seed and oil of avocado, olive and safflower.
Types of Polyunsaturated Fats
The types of PUFA are Omega-3 Fatty Acid or n-3 or w-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acid or n-6 or w-6. The three types of omega-3 fatty acids are linoleic acid (LA); Eicosapentaenoic Acid (EPA); Docosahexaenoic Acid (DHA); Alpha-Linolenic Acid (ALA). Major food sources of Omega-6 Fatty Acids are oils of palm, soybean, rapeseed, and sunflower.
Foods containing omega-6 fatty acids are eggs, whole grain foods, nuts, pumpkin seeds, pine nuts, walnuts. Other sources include oils of corn, safflower, canola, primrose. Dietary recommendation of omega-6 fatty acid is 5-10%. Major Food sources of EPA + DHA are fish oils and krill oil.
Dietary recommendation for EPA + DHA is 0.250-2 gram per day. Plant-derived oils like walnut oil, edible seeds, algal oil, flaxseed oil, clary sage seed oil, Sacha Inchi oil, Echium oil, and hemp oil are food sources for ALA.
Health Benefits of MUFA & PUFA Rich Foods
Adequate intake of fat prevents and fights various diseases.
- Long-chain omega-3 PUFA exhibits anti-inflammatory effects.
- Switching to MUFA & PUFA from unhealthy saturated fats decreases the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD).
- Reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Beneficial effects of ù-3 PUFAs on cardiovascular diseases have been noted. It reduces inflammation, inhibits platelet activity, decreases oxidative stress, exert anti-arrhythmic effects, and improve triglyceride levels, both in patients with heart disease and the general population.
- n-3 PUFAs are considered beneficial in order to boost moods and alleviate mental illness.
- Studies elucidate the anti-cancer effects of ù-3 PUFAs in prostate cancer whereby DHA exerts anti-neoplastic effects.
- Fats as per dietary recommendation improves digestion and protects the brain.
- Omega-3 fatty acids like fish oil helps in normal fetal development and cardiovascular protection.

Difference between MUFA & PUFA
While both MUFA & PUFA has 9 calories per gram and both are healthier than animal saturated fat, there are significant differences. MUFA has one double bond in the fatty acid chain while PUFA has two or more. Thus MUFA has higher melting point. MUFA is considered healthier than PUFA.
MUFA and PUFA as per the dietary recommendation helps in biochemical processes associated with nerves, brains, heart, digestion, and cell maintenance. Maintain the energy ratio where calorie expenditure should be more or equal to calorie intake. Wise choice of food items can make you relish your favorite dishes. Moderation is the key as disproportionate fat intake can cause chronic ailments.














