- FACTS ON Safety at Work - (https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/workercomp/cwcs/definition.html)
What is a Work-related Injury?
Work-related injury or illness occurs when workplace events or exposures, directly result in injury or illness. A work-related injury can also happen when the work environment makes worse a previously existing condition in a worker.
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), an agency of the US Labor Department defines work environment as “the establishment and other locations where one or more employees are working or are present as a condition of their employment. The work environment includes not only physical locations, but also the equipment or materials used by the employee during the course of his or her work.”
Work-related Injuries - Facts and Figures
According to the International Labor Organization (ILO) statistics,
- Approximately 2 million men and women die as a result of work-related injuries and illnesses annually
- Globally, an estimated 270 million occupational accidents and 160 million work-related diseases occur each year
- Occupational exposure to hazardous chemicals accounts for about 450,000 deaths annually; 10 percent of skin cancers are caused by work-related exposures
- Exposure to asbestos at workplace accounts for approximately 100,000 deaths annually
- Silicosis (lethal lung disease caused by exposure to silica dust) affects tens of millions of workers across the world in occupations such as mining, stone cutting and slate pencil cutting
- Construction sites account for a major proportion of work-related accidents and deaths; according to ILO statistics, 1 out of every 6 major accidents occurs at a construction site
- Around 60,000 fatal accidents occur in construction sites across the world annually i.e., 1 fatal accident every 10 minute
- Nearly 30 percent of construction site workers suffer from back pain and musculoskeletal problems
- Nearly 4% of the world’s gross domestic product (GDP) is lost due to cost of injury, death and disease, absence from work, disability and survivor benefits and sickness treatment
- Younger workers are at great risk of serious non-fatal accidents due to a combination of lack of experience, lack of physical and emotional immaturity, ignorance of workplace hazards and poor safety and health-training measures
- The older workers need more days away from work to recover
- Aging may be accelerated by certain occupations involving handling heavy loads, untimely work shifts, exposure to high noise levels and outdoor work in extremes of temperature
- The World Day for Safety and Health at Work is observed annually on 28th April, a date that was initially established by the ILO in 2001 and 2002.
According to Juan Somavia, who was ILO Director General from March 1999 to September 2012, “There has been a sign of progress on many fronts in the world of work. But work-related deaths, accidents and diseases, are still major causes for concern. Decent work must also be safe work.”
The ILO has always refuted the notion that injury and illness “go with the job”. Prevention works. During the course of the 20th century, developed nations witnessed a significant decrease in serious injuries due to concerted efforts and advances in making the workplace safer and healthier. The biggest challenge is to extend these measures to benefit the whole working world.
What are the Common Types of Work-related Injuries?
Serious workplace injuries are a common occurrence. Some accidents and injuries occur across all occupational sectors although different types of jobs pose a series of hazards unique to the specific job. For example, a construction worker is at a higher risk of falls while an office worker is much less at risk for burns than a chef.
Some of the most common work-related accidents and injuries include the following:

- Falls and trips – minor injuries to serious ladder fall injuries in construction sites
- Muscle strains and pain especially neck and back strains
- Repetitive strain injury caused by forceful repetitive activity or bad posture
- Cuts and bruises
- Getting hit by falling objects – can cause minor wounds or major conditions such as blindness or concussion
- Crashes and collisions involving drivers or operators of vehicles, cranes and forklift trucks in construction sites or warehouses
- Building collapse in construction sites
- Inhalation of toxic fumes and exposure to hazardous chemicals
- Exposure to loud noise, leading to loss of hearing
- Contracting of disease from patients in the hospital
- Muscle sprain or injury while maneuvering a patient
- Walking into objects such as furniture, doors and walls, resulting in minor to serious injuries
- Violence and altercations at work resulting in bodily injuries
What are the Causes of Work-related Injuries?
Mark Twain once said, “It is better to be careful 100 times than to get killed once.” It is estimated that 80 of every 100 accidents occurring in the workplace are directly due to the fault of the person involved in the incident. Some of the common “root” causes of workplace-related accidents include the following:
- Tiredness and over-exertion
- Using incorrect technique or poor equipment
- Poor housekeeping leading to unclean surroundings, dirty and slippery floors and a general lack of orderliness exposing workers to increased risk of injuries and illness
- Frequent mental distractions increasing the chances of serious errors
- Lack of preparation and ignorance of hazards involved and poor safety training
- Taking shortcuts due to laziness and increasing the risk of catastrophic accidents especially while handling dangerous machinery or lethal chemicals
- Overconfidence leading to carelessness

A conscious effort is essential each and every day in the workplace to ensure that the aforementioned mistakes are avoided. The life of not only the individual, but also the person’s co-workers and the reputation and well-being of the organization is at stake.
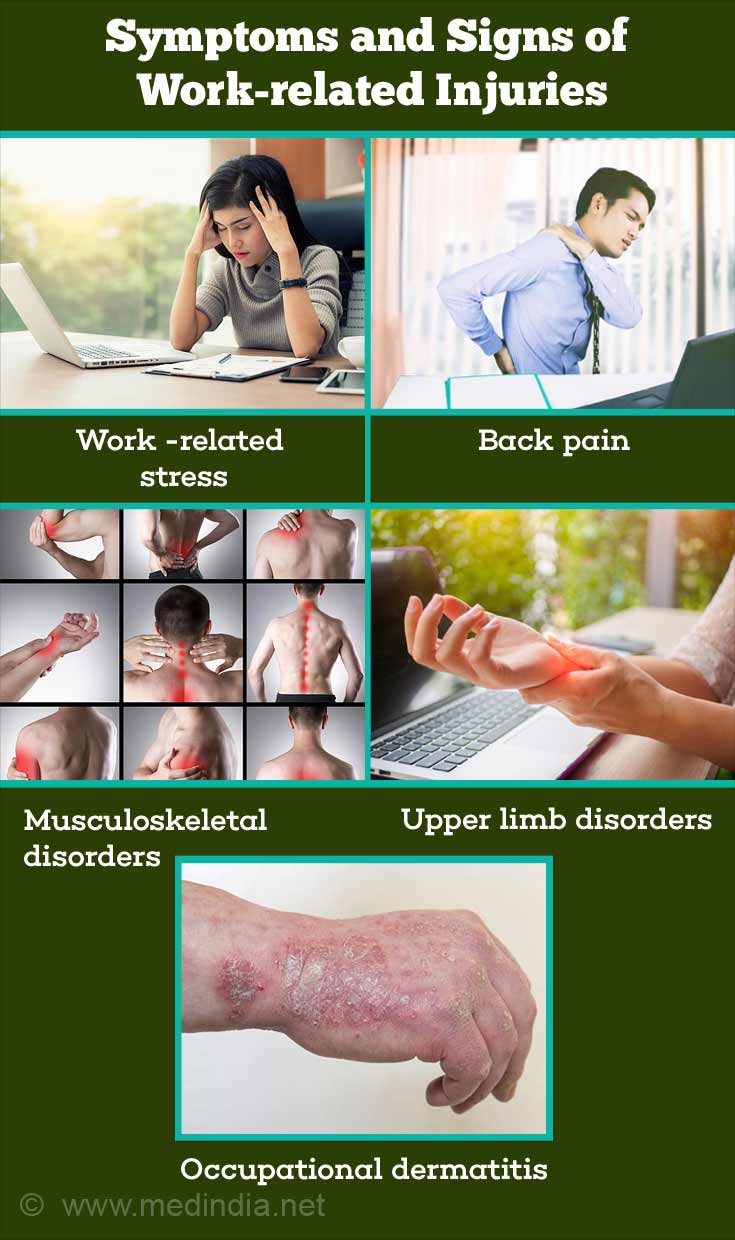
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Work-related Injuries?
Some of the commonly encountered work-related injuries and illnesses include the following:
- Work-related stress
- Back pain
- Musculoskeletal disorders due to uncomfortable posture, handling heavy loads, and overexertion
- Upper limb disorders - affecting the arm and shoulder, forearm, elbow, wrist, hand and fingers. Common symptoms include aches and pain, stiffness, tenderness, weakness, tingling, numbness, cramps, or swelling.
- Occupational dermatitis (skin disorder) due to handling of chemicals
- Occupational asthma due to exposure to smokes, fumes and dust
- Exposure to excessive noise levels and hearing loss
- Constant viewing of display screens and monitors, leading to eye strain
What are the Best Ways to Prevent Injury at Work?
It is the obligation of the employer to ensure the safety and well-being of the worker. The following measures must be followed to ensure the same.
Employer’s Responsibilities
- Carrying regular assessments regarding risks to health and safety standards of workers in the workplace and having safety norms and practices in place as appropriate
- Provision of ergonomically designed furniture to minimize occurrence of back pain and musculoskeletal pain
- Provision of adequate safety training, education on hazards and correct techniques of handling as well as optimal usage of machinery and equipment
- Ensuring proper functioning and well-maintained equipment
- Education on fitness, healthy lifestyle and work-life balance
- Having a system in place where work-related injuries or illnesses are brought to the notice of the authorities with appropriate management, which includes reassigning of duties
- Ensure regular breaks from constant activity such as staring at monitors or noisy work environment to minimize eye strain or hearing loss
- Periodic breaks to reduce risk of fatigue and overstrain and consequent errors
- Ensure safety measures to minimize occupational exposures and prompt evaluation and treatment of the same
- Proper and good housekeeping practices to ensure safe working environment
- Referral to appropriate specialist for advice on management and prevention of recurrence in future
- Identification of source of stress at work with risk assessment and strategies to handle the same with friendly and understanding managers
Responsibility of Employees/Workers
Although employers are duty bound to provide a safe working environment for their workers, it is the responsibility of the individual to be careful and avoid taking undue risks that may endanger the person’s safety as well as the safety of co-workers.
- Avoid operating heavy machinery and equipment if tired and unwell
- Follow safety precautions diligently, such as, wearing helmets at construction sites
- Avoid taking shortcuts to complete a task soon without knowing the risks or dangers involved
- Report any work-associated stress to authorities sooner than later for appropriate action
- Avoid being distracted, focus on the work and take a break if necessary to refresh yourself
- Do not handle equipment or machinery without proper training or knowledge of the hazards and correct technique of handling them
What is Workers’ Compensation?
Workers’ compensation is insurance amount paid by the employer to workers who are injured or fall ill on the job. By this means, workers are given free/partial medical care and benefits while off work due to the injury.
Under workers’ compensation, the worker is automatically entitled to insurance for injury sustained on the job and in return, the worker will not sue the employer for his illness or injury.

Workers’ Compensation - Facts
- All employers should pay workers’ compensation
- Workers’ compensation also covers long-term illness (eg asthma) due to work environment in addition to accidents or incidents
- The employer pays the compensation to private insurance companies
- The cost to the employer depends on the gross payroll, type and severity of injury and the frequency of its occurrence in the organization
- Employees could still sue their employer if injury was inflicted intentionally or the job was outside the routine duties of the worker
- Employer need not pay compensation if the injury was self-inflicted, occurred outside the workplace, occurred during the commission of a crime or if the worker violated company rules
- The employer should not discriminate against workers who file for compensation
- The employer should re-train the worker upon return to prevent such incidents in future