- Thunderclap Headaches: Mayo Clinic- (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/thunderclap-headaches/symptoms-causes/syc-20378361)
- Thunderclap Headaches: American Migraine Foundation - (https://americanmigrainefoundation.org/understanding-migraine/thunderclap-headaches/)
- Silberstein SD, Young WB. Headache and Facial Pain: Benign Thunderclap Headache. Textbook of Clinical Neurology (3rd Edition), 2007.
- Waldman SD. Primary Thunderclap Headache. Atlas of Uncommon Pain Syndromes (3rd Edition), 2014.
- Valade D, Ducros A. Headache: Thunderclap Headache. Handbook of Clinical Neurology, 2010.
- Ducros A, Bousser M-G. Thunderclap Headache. BMJ 2013; 346: e8557. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.e8557.
What are Thunderclap Headaches?
Thunderclap headaches, as the name suggests, strike like a bolt from the blue, just like a clap of thunder, without any warning. This rare headache disorder is severe and explosive in nature, often appearing without any apparent trigger. The intense pain peaks within 60 seconds and lasts for at least 5 minutes. These headaches warn of potentially serious underlying conditions such as brain hemorrhage and other complications. Thunderclap headaches require prompt medical attention.
Epidemiology of Thunderclap Headaches
The annual global incidence of thunderclap headaches is estimated to be 43 per 100,000 adults in the developed countries. There is a corresponding sparsity of data in the developing countries. A recent study from Paris, France suggests that 1.5% of all headache patients could be due to thunderclap headaches.
Types of Thunderclap Headaches
Thunderclap headaches can be classified into two types:
- Those caused by diseases of the vascular system, head injury, or rare structural changes in the brain.
- Those lacking a clear-cut cause, which upon medical evaluation, are regarded as benign and not considered to be dangerous.
However, abrupt severe headaches triggered by physical activity, including sexual activity or straining during defecation, or headaches following head injury, are regarded as being potentially dangerous and require immediate medical evaluation. Moreover, immediate medical attention should be sought if thunderclap headaches are accompanied by loss of vision or sensation, fever, weakness, confusion, slurred speech, or cognitive impairment.
What are the Causes of Thunderclap Headaches?
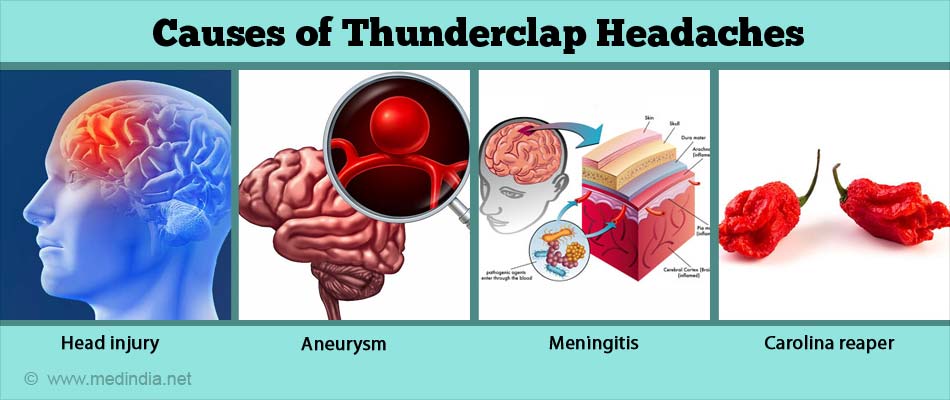
There are many causes of thunderclap headaches. The major ones are highlighted below:
- Ischemic stroke
- Hemorrhagic stroke
- Head injury
- Rupture of an artery or aneurysm
- Blockage of a blood vessel in the brain
- Inflammation of a blood vessel (vasculitis)
- Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome (RCVS)
- Infections – meningitis / encephalitis
- Pituitary apoplexy
- Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
- Severe elevation of blood pressure (hypertensive crisis)
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage/ aneurysm
- Cervical artery dissection or tearing
- Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis
World’s Hottest Chilli: An Uncommon Cause of Thunderclap Headaches!
The Carolina Reaper is the world’s hottest chilli since 2017. With reference to “hotness”, the chilli can be as high as 2.2 million on the Scoville heat units (SHU) scale. This is huge when compared to a standard jalapeno chilli, which is no more than 8,000 SHU. As an anecdotal evidence, a 34-year-old man developed skull-crushing thunderclap headaches while participating in a chilli-eating contest in New York. He developed these headaches immediately after consuming a Carolina Reaper and had to be rushed to the Emergency Room (ER) for emergency medical intervention. It took five weeks for him to recover fully.
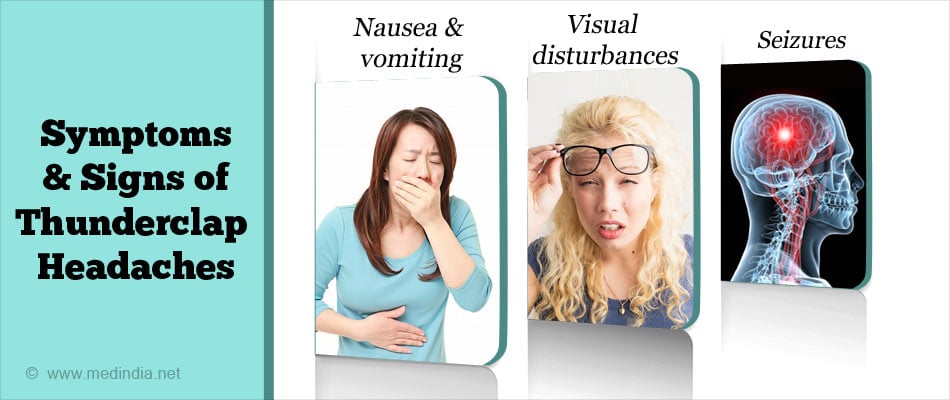
What are the Symptoms and Signs of Thunderclap Headaches?
The cardinal symptoms of thunderclap headaches are the rapid onset and intense pain peaking within 60 seconds. There are several other symptoms and signs of thunderclap headaches, which are listed below:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Visual disturbances
- Confusion
- Fainting (syncope)
- Weakness
- Loss of sensation
- Loss of ability to think or focus
- Seizures
- Fever

How do you Diagnose Thunderclap Headaches?
Thunderclap headaches are usually diagnosed in a stepwise manner, from simple to complex diagnostic approaches. These are briefly discussed below:
- Physical Examination: The patient is first evaluated by a thorough physical examination. Clinical signs and symptoms highlighted above can be supported by measuring various parameters like blood pressure, temperature, eyesight and others.
- Lumbar Puncture: This procedure is also known as a spinal tap. The technique involves insertion of a needle into the spinal column in the lower back (lumbar region) to withdraw CSF. The nature and properties of the CSF are analyzed in the laboratory, and if there is any infection in the brain or spinal cord, it can be detected.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: A CT scan involves taking serial X-ray images of the brain from different angles and then processing the photos in a computer to generate high resolution images of the brain in the form of slices so that all the areas of the brain can be visualized and analyzed. A CT scan is usually sufficient to pinpoint the underlying cause of the headache. Importantly, CT scans are very sensitive for detecting subarachnoid hemorrhages.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI is a very accurate imaging technique that is based upon the principle of magnetic resonance. Unlike CT scans, which uses X-rays, MRI does not involve any radioactive substances. MRI uses radio waves, a magnetic field, and a computer to scan the body parts to look for structural abnormalities. Here, the patient is placed within a MRI machine for generating the images. In case a CT scan fails to detect any abnormality, an MRI is usually recommended.
- Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA): MRA is a type of MRI that looks specifically at problems of the arteries, such as an arterial tear or dissection. A variation of MRA is magnetic resonance venography (MRV), which can accurately diagnose problems of the veins such as cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Both MRA and MRV are powerful tools for detecting any vascular abnormalities associated with the arteries are veins respectively.
How do you Treat Thunderclap Headaches?
There are several options that are available for treating thunderclap headaches. If an underlying cause can be found, it has to be treated. Treatment measures include the following:
- Painkillers: Also known as analgesics, these medicines are prescribed for relieving pain. Some examples include paracetamol and ibuprofen or a combination of both. Naproxen can also be taken. These medicines provide symptomatic relief of the pain, but does not treat the underlying cause.
- Antihypertensives: In case where high blood pressure (hypertension) is the underlying cause of thunderclap headaches, drugs such as calcium channel blockers can be used. These include drugs such as amlodipine, nifedipine, verapamil, diltiazem, nicardipine, amongst others. Treating hypertension can prevent the occurrence of these headaches.
- Surgery: In some circumstances, surgery may be recommended to treat the underlying condition, especially when medicines are ineffective. Surgical intervention can be used to repair tearing or dissection of an artery. It is also recommended for repairing a ruptured aneurysm.
How do you Prevent Thunderclap Headaches?
From the foregoing discussion, it is clearly evident that in most cases thunderclap headaches cannot be prevented. However, diseases like hypertension should be kept under control by regularly taking the medications. Risky behavior such as consuming hot and spicy foods (especially hot chillies like Carolina Reaper!) must be avoided. Moreover, a healthy diet and a regular exercise regimen for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health should be followed. These approaches could help to keep thunderclap headaches at bay.