- Spinal cord injury - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/spinal-cord-injury/basics/definition/con-20023837?p=1)
- Levels of Injury - (http://www.spinalinjury101.org/details/levels-of-injury)
What is Spinal Cord Injury?
The spinal cord and brain together constitute the central nervous system. The spinal cord contains various nerve fibers through which impulses get transferred from the brain to the body and vice versa. Injury to the spinal cord can result in an altered function, either temporarily or permanently; this is known as spinal cord injury.
Spinal cord injury causes a change in the strength, sensation and functions below the level of the injury. Spinal cord injury can significantly affect the quality of life. The vertebral column level at which the spinal cord is injured and the severity of injury are the key factors which decide the function of the limbs. The roles of treatment and rehabilitation are vital in case of spinal cord injuries.
What are the Causes of a Spinal Cord Injury?
The causes of spinal cord injury are:
- Road Traffic Accidents (RTAs): RTAs are the main cause of a spinal cord injury.
- Falls: Fall in elderly can cause spinal cord injury.
- Alcohol: Consumption of alcohol can contribute to spinal cord damage.
- Acts of Violence: Violent acts like gunshots and stabbing are also contributors of spinal cord damage.
- Sports Injuries: Injuries during sports can damage the spinal cord.
- Diseases: Diseases like osteoporosis, cancers, infections and arthritis can cause spinal cord injuries.

The people at risk of spinal cord injuries are:
- Males
- Anyone between 16-30 yrs age group
- Elderly people
- People with risky behaviors
- People with bone and joint diseases
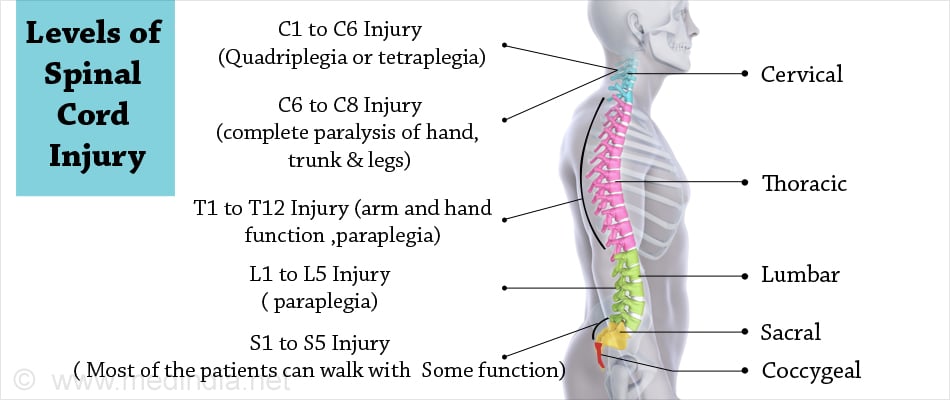
What are the Levels of Spinal Cord Injury?
Depending on the vertebral column level at which the spinal cord is injured, the manifestations vary. The higher the level of injury the more the dysfunction.
Cervical Level
- C1-C4 level: If the spinal cord is injured at this level, it causes quadriplegia or tetraplegia (paralysis of all the four limbs). The patient cannot breathe and may require mechanical ventilation. The patient may not have control over the bowel and bladder. These patients need complete personal care.
- C5 Level: This causes an incomplete or complete paralysis of trunk, legs, wrist and hand.
- C6 Level: The injury at C6 level can cause an incomplete or complete paralysis of hand, trunk and legs.
- C7 and C8 Level: At this level of injury, some function of the hand is present while the trunk and legs are affected.
Thoracic Level
- T1 to T12: The arm and hand function normally. It can result in paraplegia where both of the legs are paralyzed. They might need to use a manual wheelchair.
Lumbar Level:
- L1 to L5: It causes some functional loss in the legs and hip.
Sacral Level:
- S1 to S5: Some functional loss occurs in the legs and hip. Most of the patients can walk.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Spinal Cord Injury?
The symptoms and signs depend on the level of the spinal cord injury and the severity of the injury. Spinal cord injury can result in any of the following symptoms:
- Loss of movements in the limbs
- Loss of sensation like touch, pressure, vibration, heat and cold
- Loss of control over the bowel and bladder
- Difficulty in breathing and coughing
- Reduced sexual function and fertility
- Pain
- Weakness or paralysis
- Numbness
- Inability to walk

How do you Categorize a Spinal Cord Injury?
The spinal cord injury can be categorized based on the severity of the injury as below:
- Complete Injury: It is a total loss of sensory (feel) and motor (movement) function below the level of the injury.
- Incomplete Injury: It is a partial loss of sensory and motor function below the level of the spinal cord injury.
How do you Diagnose a Spinal Cord Injury?
Carefully noting down the history of the injury and examining sensory and motor functions are essential to find the level and severity of the injury.
The following are a few investigations that will help to find the internal cause of the spinal cord injury.
- X-ray: It is a widely available test. The images from x-rays help to find if there are any vertebral diseases, fractures, degenerative diseases or tumors. But x-rays can miss the spinal cord injury. In such cases, advanced imaging techniques are required.
- Computerized Tomography (CT scan): It helps to find any abnormalities in the vertebrae and gives more detailed images than x-rays.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): It helps to find problems in the bones due to spinal cord injuries as well as find any masses or blood clots that maybe compressing the spinal cord.
How do you Treat a Spinal Cord Injury?
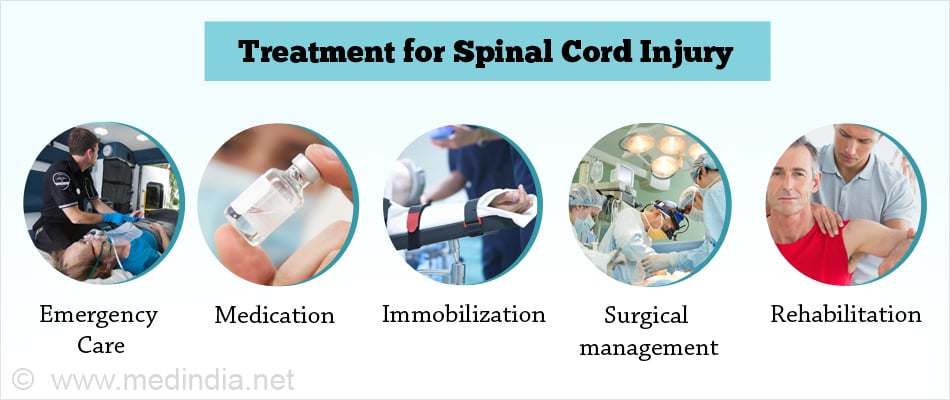
- Emergency Care: Emergency action before reaching the hospital includes maintaining the airway, breathing and circulation. Immobilization to prevent further damage is necessary.
- Medications: An injection methyl prednisolone is given within 6-8 hours after the injury. It helps by preventing the inflammatory reaction at the injured site as well as by reducing further damage. Medications to improve blood pressure are also necessary.
- Immobilization: Immobilization of the neck and spine are necessary before the surgical management to prevent further damage. Neck collar and traction are useful to immobilize the spine.
- Surgical management: It may be required to remove the herniated disc, broken fragments of bone and to stabilize the spine.
- Rehabilitation: A physiotherapist helps in rehabilitation. It is essential to maintain the retained muscle function, to redevelop the motor activity and to be able to perform day to day activities.
How do you Prevent a Spinal Cord Injury?
Following are a few measures to be taken to prevent a spinal cord injury.
- Safe driving: Follow the traffic rules, use car seat belts, use helmets on bikes and do not drink and drive to prevent accidents and spinal cord injury.
- Prevent falls: Block staircases to prevent access to toddlers and young children. Put non-slip mats near the bathrooms to prevent falls.
- Diving: Check the depth of water before diving. Avoid diving in shallow water. The depth of the pool should be a minimum of 9 feet to dive.
- Safety during sports: Wear suggested safety gear.

- Follow the traffic rules
- Use car seat belts
- Use helmets
- Avoid drinking and driving