- Leksell L. The stereotaxic method and radiosurgery of the brain. Acta Chir Scand. 1951; 102(4): 316-9. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14914373)
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery - Mayo Clinic - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/stereotactic-radiosurgery/about/pac-20384526)
- Radiosurgery for Brain Tumors - Cancer Research UK - (https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/brain-tumours/treatment/radiotherapy/radiosurgery)
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery - CyberKnife® - Medline Plus, National Institutes of Health (NIH), USA - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007274.htm)
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy (SBRT) - RadiologyInfo.org - (https://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=stereotactic)
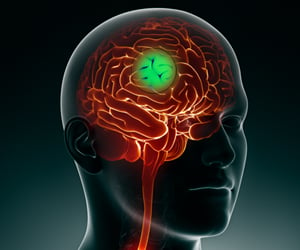
What is Radiosurgery?
Radiosurgery, as the name suggests, is surgery using radiation, without the need for surgical excision. The term “radiosurgery” was originally defined by the Swedish neurosurgeon Dr. Lars Leksell as, “a single high dose fraction of radiation, stereotactically directed to an intracranial region of interest”. The word “stereotactic” refers to a set of three-dimensional coordinates that enables the surgeon to pinpoint the exact location of the surgical area. Hence, this treatment is known as Stereotactic RadioSurgery (SRS). Stereotactic RadioTherapy (SRT) is defined as High dose fraction of Radiation delivered to Intracranial Region of Interest in 4-5 sessions.
Radiosurgery or stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) uses 3D imaging for sharply focusing beams of ionizing radiation to specific areas of diseased tissue, without damaging surrounding healthy tissue. It is primarily used for treating cancer of the brain, spinal cord, and other parts of the body. When SRS is used to treat cancer outside the central nervous system (CNS), it is called stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) or stereotactic ablative radiotherapy (SABR).
What are the Devices used for Radiosurgery?
Three types of radiosurgery are used to treat cancers of the CNS and other parts of the body:
Linear Accelerator (LINAC): LINAC is the device, primarily used for external beam radiation treatments for cancer. It is used to treat all body parts and delivers high-energy X-rays or electrons to the tumor. There are two common brands of LINAC machines:
- CyberKnife®: It is a Radiation therapy device manufactured by Accuray Inc., Sunnyvale, California, USA. It is a non-invasive procedure that enables oncologists to deliver targeted, high doses of radiation to a broad range of tumors throughout the body.
- TrueBeam®: It is a Radiotherapy device manufactured by Varian Medical Systems, Palo Alto, California, USA. It is an advanced medical LINAC device that is fully-integrated for image-guided radiotherapy and radiosurgery for treating cancer anywhere in the body. These machines can perform SRS in a single or multiple sessions. The latter is termed fractionated SRS.
Gamma Knife®: It is a non-invasive SRS instrument that uses up to 201 sources of Cobalt 60 that emits precisely focused beams of Gamma radiation for treating malignant and non-malignant brain tumors. This device is an alternative to traditional brain surgery or whole brain radiation therapy for treating complex conditions.
Proton Therapy: Also known as “Proton beam therapy”, it is a type of radiation therapy that uses protons instead of X-rays to treat cancer. A proton is a positively charged particle. High energy protons can destroy cancer cells. Protons have the potential to destroy only the tumor region while sparing the normal tissues. This property of Proton is very useful in treatment of SRS and is available only in a few research centers in USA. However, Proton therapy will be coming for Clinical use in India in Early 2019. Proton therapy can be used alone, or in combination with X-ray radiotherapy, surgery, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.