- Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) - (https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/adhd/diagnosis.html)
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) - (https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/attention-deficit-hyperactivity- disorder-adhd/diagnosis/)
- Mind wandering during attention performance: Effects of ADHD-inattention symptomatology, negative mood, ruminative response style and working memory capacity - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5524389/)
What is Mind Wandering?
Mind wandering is a spontaneous shifting of attention of thoughts from a primary task that can happen in varying degrees. It is an unintentional and unrelated shift that occurs where the mind tends to regale in varied thoughts which can disrupt the ongoing task performance.
Mind wandering was earlier known as day dreaming, fantasy or flights of fancy. People often spend 46.5 percent of their waking time “mind wandering” during everyday tasks, temporarily losing track of time, place, or current task goals. Individuals tend to engage in more sorrowful and future related thoughts during mind wandering.
However, recent research indicates that deliberate mind wandering can be used to alleviate boredom or generate creative ideas.
There is a marked resemblance between symptoms of mind wandering and mental illnesses such as schizophrenia [a serious mental illness which impacts a person’s ability to perceive the world around them] and ADHD [Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder]. This could be due to the fact that similar areas of the brain cortex are involved.
What are the Causes of Mind Wandering?
The exact causes of mind wandering are not yet understood. Researchers say that a network of neurons called the default mode network (DMN) in the brain had been associated with mind wandering. The default mode network is a large scale brain network of interacting brain regions in the areas of the cortex, especially the cingulate gyrus which deals with emotions and behavior. This network is most active when a person is resting and when no external tasks demand a person’s attention. The default mode network consistently decreases its activity when compared with activity during demanding tasks. These networks are very similar across all age groups.
The discovery of the default mode network has reignited a longstanding interest in the better understanding of the brain's ongoing intrinsic activity.
What are the Symptoms of Mind Wandering?
- Lack of awareness of the surrounding environment due to preoccupation with own thoughts. This may lead to accidents such as banging into objects or people, falling down a step of stairs, ignoring traffic signals and so on. Lack of driver awareness is a key risk factor for most motor vehicle accidents. This endangers the lives of both the driver and others on the road.
- Comprehension failure during reading and listening. A student or an office person may not fully understand things being explained to them leading to errors or may be unable to listen or carry out instructions. This is not due to lack of intelligence but rather due to mind wandering.
- Inability to focus. There is a reduced capacity to focus on the task at hand and people who allow their minds to wander may ignore what is happening around them. This can be misinterpreted as being uninvolved or lacking interest in the task. They also have difficulty in sticking to tasks that are tedious or time consuming, and in organizing or concentrating on daily jobs. They may end up making careless mistakes, and their work might seem messy and careless. They have difficulty staying on a topic while talking, and do not listen to others or follow social norms.
- Lack of attention or having a short attention span in following instructions or executing a plan. They are very easily distracted from the main task at hand, and are constantly changing tasks. They continually start new tasks before finishing old ones.
- Depression - A common finding in such people, this may be a consequence of mind wandering.
- Sleep disturbances - They often find it difficult to sleep at night and have irregular sleeping patterns.
- Continually losing or misplacing things due to forgetfulness.
- Inability to deal with stress.
- Risky behavior in activities, often with little or no regard for the personal safety or the safety of others. This includes not paying attention while crossing roads, driving dangerously, and performing dangerous experiments.

How do you Diagnose Mind Wandering?
Normally, a doctor will record the patient’s complete medical history with special focus on mental symptoms to rule out other anomalies. A routine physical checkup is also done. Previously, diagnosis was based on a psychologist’s assessment, but the following tests, which help aid diagnosis, are more accurate.
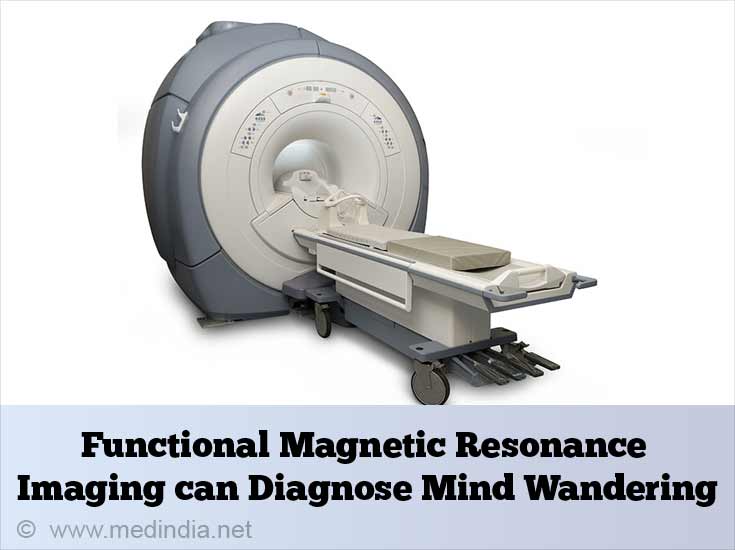
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging or fMRI is a non- invasive way to assess brain functioning. The test uses MRI changes associated with brain activity to identify brain areas with corresponding mental behavior. It is used to measure the metabolic changes in the brain.
When an area of the brain is in use, blood flow to that region also increases along with an increase in neuronal activity. Interestingly, similar brain patterns are also associated with reduced receptiveness to external stimuli. Psychologists are starting to use functional magnetic resonance imaging to observe changes related to mind wandering in the brain and reduce their reliance on verbal reports.
The Imaginal Processes Inventory developed by Jerome Singer and John Antrobus provides information on the daydreaming characteristics of an individual. It is a questionnaire which assesses the experience on three dimensions: 1) how vivid the person's thoughts are 2) how many of those thoughts are guilt or fear based and 3) how deep into the thought process a person goes. This method helps in providing data without embarrassment to the person as they may have difficulty in verbally describing them.
How do you Treat Mind Wandering?
- Improve mind awareness by being fully aware of your thoughts, actions and feelings in the present moment. Meta-awareness is the concept of taking awareness itself as an object of attention. Mindful awareness can be developed through the practice of certain meditations and exercises. Mindfulness is simply focusing completely on what you are doing at the moment and observing all of the physical and emotional sensations you are experiencing in that moment. You can practice mindfulness during daily activities such as eating (by concentrating on the flavors and texture of food), brushing teeth, shaving, praying and so on.
- Meditation for 10-20 minutes daily will improve attention span significantly. There are many different types of meditation including Zen meditation [a form of Buddhist meditation that originated in China in the 6th Century], Transcendental Meditation [a technique for avoiding distracting thoughts and promoting a state of relaxed awareness derived by Maharishi Mahesh Yogi from the ancient Vedic tradition of India], Om meditation [the daily chanting of Om mantra, said to give peace to your mind, body and soul], Shine Meditation or Samadhi, and Chakra Meditation [to open up and align the 7 chakras or wheels of energy throughout the spine, starting from the base of the spine and ending at the crown of the head].
- Perform Yoga and Tai Chi concentration exercises. Yoga involves a series of both moving and stationary poses, combined with deep breathing. Pranayama, Kapalbhati and Bhastrika are some deep breathing exercises which have proved effective in mind control. As well as reducing anxiety and stress, Yoga can also improve overall health by increasing flexibility, strength, balance and stamina. Tai Chi is a self-paced, non-competitive series of slow, flowing body movements. By focusing your mind on the movements and your breathing, you keep your attention on the present. This helps clear the mind and leads to a relaxed mental state.
- Take a few massage sessions to reduce stress, relieve pain, and ease muscle tension. To enhance relaxation, you can use aromatic oils, essential oils, and scented lotions. You can also combine the massage with mindfulness or deep breathing techniques.
- Take medication if the mind wandering is associated with other serious mental problems such as depression or anxiety disorders.

How do you Prevent Mind Wandering?
- Try focusing on one thing at a time.
- Set reminders to check whether you are still focused on your task. You can also give yourself a pep talk to check whether you are still on track.
- Give your mind more to do. Research studies at University College London show that adding deliberate distractions actually reduces distractibility.
- Daydream during breaks. Think about something unrelated in your break time and then come back to your task.
- De - stress.
- Get some sleep. Lack of sleep hampers mental performance in general and reduces ability to resist both internal and external distractions. Sleep is also a very important factor for memory consolidation.
- Eat nutritious food. Studies show that certain food items, such as sugar, refined carbohydrates, food coloring, additives, caffeine and wheat or dairy products (if intolerant) can aggravate mental conditions.
- Create a routine. Try to follow the same schedule every day, from morning till night.
- Get organized. When things are in the right place, precious time is saved searching for them which can prevent the mind from wandering and help avoid unnecessary stress.