How is Nephrotoxicity Diagnosed?
It is important to diagnose nephrotoxicity at an early stage. The physicians must be aware of nephrotoxic potential of drugs and the risks involved.
Nephrotoxicity can be diagnosed with simple blood tests. However, these assessments help when the damage to kidney is extensive. These tests could include:
- Serum creatinine levels in blood
- Measurement of BUN (Blood urea nitrogen)
- Creatinine clearance
- Glomerular filtration rate
The use of biomarker helps in assessing nephrotoxicity at an early stage. Some of the biomarkers include:
- Type IV Collagen - an important biomarker of nephrotoxicity- helps to indicate changes in glomerulus
- Albumin- a high molecular weight protein used to indicate kidney damage for early diagnosis of changed glomerular filtration and diabetes
- Transferrin - helps in transporting iron, is a strong indicator of glomerular damage
- Cytokines - these biomarkers are involved in glomerular and tubular damage and repair
- NGAL (Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) - a sensitive biomarker for diagnosis of kidney injury
How do you Treat Nephrotoxicity?
Nephrotoxicity can be treated by methods listed below:
- The renal failure can be managed by maintaining the fluid volume in body, start dialysis or adjust drug doses
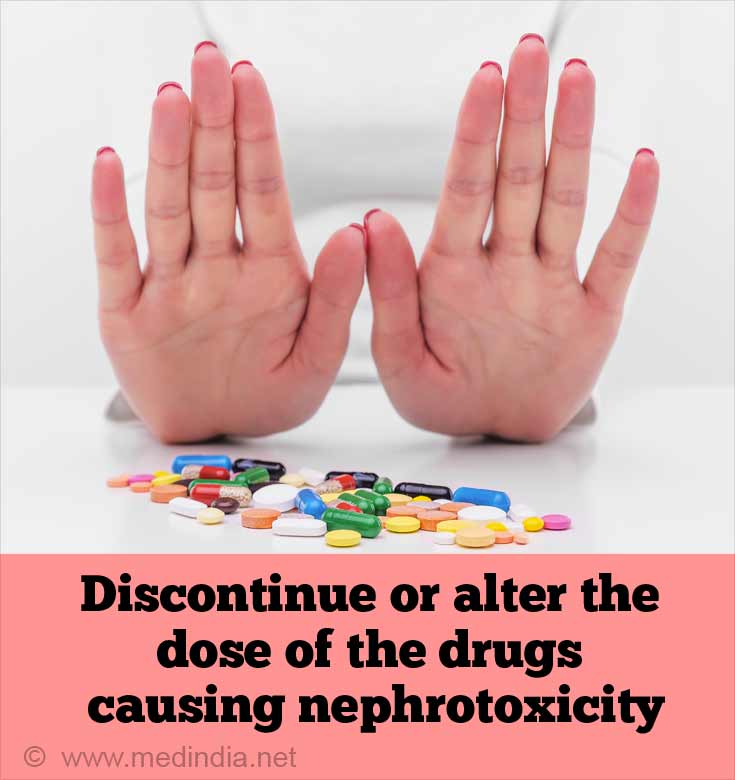
- The drug causing nephrotoxicity must be discontinued or its dose be altered
- In some conditions, steroid therapy may help
- Maintaining electrolyte balance
What are the Common Risk Factors for Drug-induced Nephrotoxicity?
The common risk factors include:
- Age above 60 years
- Patient already suffering from Renal insufficiency
- Sepsis
- Heart failure
- Diabetes
- Patients with dehydration and extracellular volume depletion
- Increased uric acid level or Hyperuricemia
- Prior exposure to radio contrast agents for doing X-rays or CT scan.
How do you Prevent Nephrotoxicity?
- Limit intake of NSAID drugs and limit painkillers
- Look out for words in prescription leaflet which indicate “could cause nephrotoxicity” and avoid using these drugs
- Use alternate drugs which are non-nephrotoxic drugs
- Monitor renal function during therapy and adjust dosage of drug depending on the vital signs
- Be aware of patient risk factors and avoid drugs which could cause nephrotoxicity