Q: Which doctor should I consult for coronary heart disease?
A: If you think you suffer from symptoms of coronary heart disease, you should consult your family physician who will recommend you to a cardiologist.
Q: Is coronary heart disease and coronary artery disease the same thing?
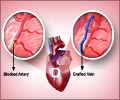
A: Yes, coronary heart disease and coronary artery disease are terms that are used interchangeably. They describe the same condition. More appropriately, coronary heart disease is a result of coronary artery disease i.e. blocks in the artery lead to damaged heart muscle and hence, coronary heart disease.
Q: What is ischemic heart disease?
A: Ischemic heart disease is the complications of the heart that arise when the arteries become narrow reducing the supply of blood and oxygen to the heart muscle. Heart murmur, heart failure, or a heart attack, are some of the complications.
Q: What happens to your body when you have coronary heart disease?
A: The first major symptom to indicate you have coronary artery disease is chest pain that occurs due to emotional stress or a physical activity. The chest pain may then be accompanied by pain that radiates to the jaw, arms, back, upper abdomen, and the back of the neck.
Q: How does smoking cause coronary heart disease?
A: The chemicals present in tobacco smoke harm the functioning and the composition of the blood vessels. The chemicals also damage the functioning of the heart resulting in the risk of coronary heart disease.
Q: Is pain in the shoulder a heart attack?
A: Not all shoulder pain is due to heart attack. To classify the shoulder pain as a heart attack, the pain in the shoulder must accompany chest pain that is due to emotional trauma or physical stress. The pain in the shoulder is a radiating pain.
Q: Is there a cure for heart disease?
A: Heart disease can be managed and treated by following the appropriate diet, making changes to lifestyle, such as avoiding smoking, performing regular exercise, taking regular medications, or through surgery (e.g. bypass surgery or catheterization). This will prevent the reoccurrence of the condition.