‘Monoenergetic X-rays would make it possible to decrease the required concentration of contrast agents by about one third with no loss of contrast.’
Tweet it Now
A team
at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) has now demonstrated that
the required quantity of these substances can be significantly reduced
if monoenergetic X-rays from a miniature particle accelerator are used."The contrast agents can sometimes be hazardous to health. Particularly in patients with kidney insufficiency, complications may arise, in some cases even kidney failure," explains Dr. Daniela Münzel, an adjunct teaching professor for radiology at TUM's Klinikum rechts der Isar. "That is why we are studying possibilities of using lower concentrations of contrast agents."
Precise X-rays
One approach to reducing the dosage has now been developed by scientists from the Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at the Klinikum rechts der Isar, working in close cooperation with the Chair of Biomedical Physics at TUM's Department of Physics.
The method, which they have described in a paper published in Nature Scientific Reports, is not based on new contrast agents. Instead it relies on special X-rays generated using the Munich Compact Light Source (MuCLS), the world's first mini-synchrotron, which was officially inaugurated at TUM at the end of 2015.
Advertisement
Close to the absorption edge
Advertisement
As a result, when using conventional broad-spectrum X-ray sources, an adequate quantity of contrast agent must always be used in order to offset this effect and obtain a sufficiently sharp image for a diagnosis. The MuCLS can generate X-rays that have exactly the optimal energy level. The capability of producing such monoenergetic X-rays has existed for some time. In the past, however, this was possible only with circular particle accelerators with a diameter of several hundred meters. In contrast, the MuCLS is comparable in size to a car.
A significant improvement
The data shows that monoenergetic X-rays would make it possible to decrease the required concentration of iodine by about one third with no loss of contrast. For gadolinium, there would even be a somewhat greater reduction. A lot more research is needed, however, before real patients can be examined with monoenergetic X-rays.
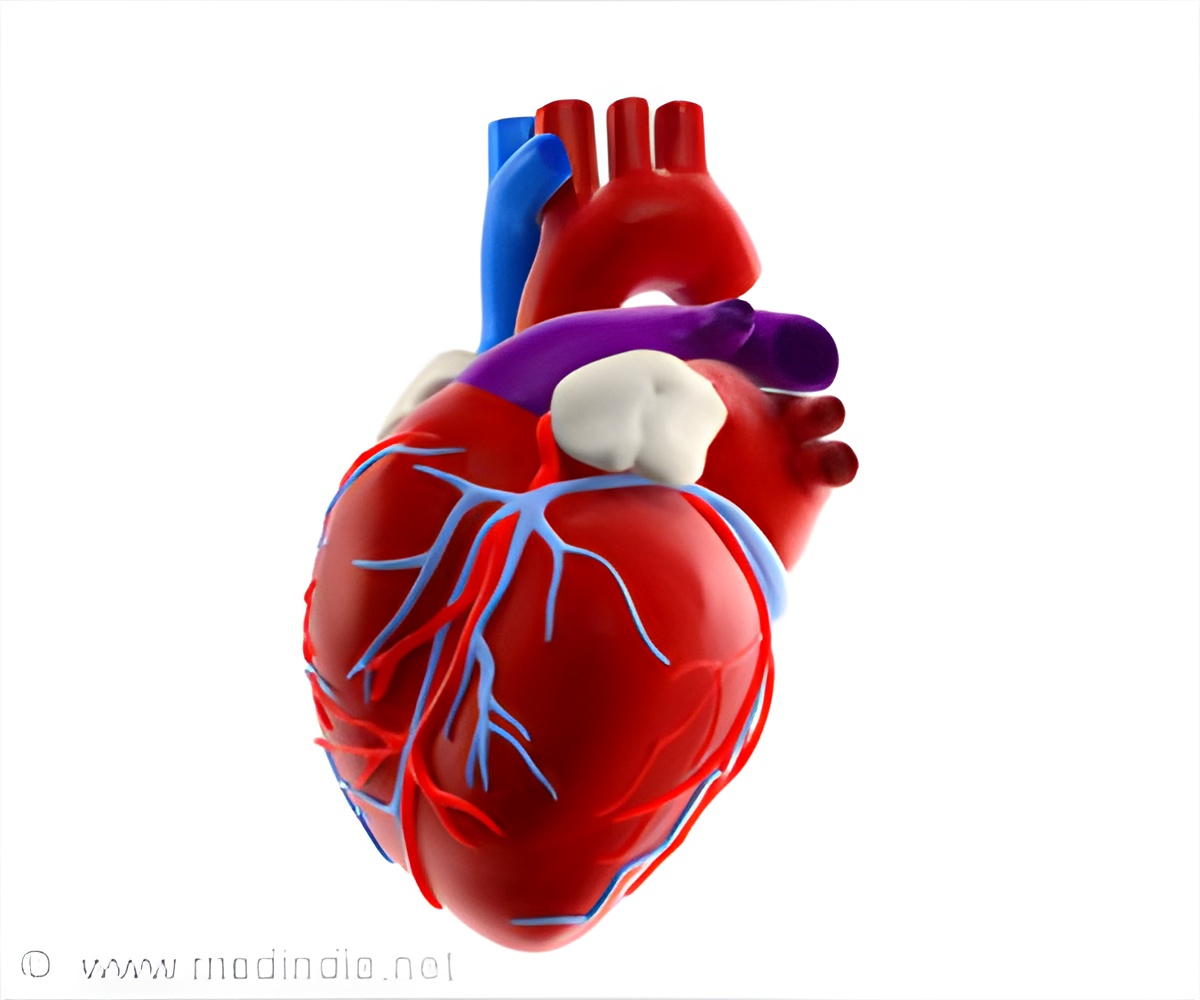
"We're still at the very beginning of the development of this technology," says Elena Eggl. The MuCLS is the very first machine of its kind. Moreover, it is designed for fundamental research, and not for examining patients. But with detailed computer simulations and tests with a pig's heart, using blood vessels dyed with iodine, the researchers were able to demonstrate feasibility of the method.
Good prospects
Franz Pfeiffer, professor of biomedical physics at TUM, sees the team's results as a promising start for medical research with the compact synchrotron: "The MuCLS offers numerous possibilities for medical applications that we plan to continue researching with our partners in medical fields."
Source-Eurekalert