As countries across the globe observed World Diabetes Day Wednesday, the World Health Organisation said the number of diabetics worldwide will be 366 million by 2030 with India alone having nearly 80 million such patients.
According to the WHO, more than 180 million people worldwide are currently suffering from the disease and India is home to over 35 million diabetics."This number is likely to more than double by 2030. In 2005, an estimated 1.1 million people died from diabetes and almost 80 percent of diabetes deaths occur in low and middle-income countries," the global health watchdog said on its official website.
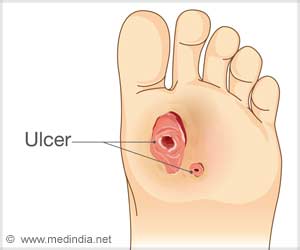
The UN body added that diabetes could damage the heart, blood vessels, eyes, kidneys, and nerves.
"Diabetic retinopathy is an important cause of blindness, and occurs as a result of long-term accumulated damage to the small blood vessels in the retina.
"After 15 years of diabetes, approximately two percent of people become blind and about 10 percent develop severe visual impairment," it added.
According to doctors, a low-income family with a diabetic loses 25 percent of its family income due to medical expenditure. Medical practitioners also expressed fear that lifestyle changes in urban areas will make the disease a huge threat.
Advertisement
Byotra said regular glucose checks, good food habits, and 30 minutes of exercise every day could help people avoid complicated health problems.
Source-IANS
SRM/P