During pregnancy and childbirth, women with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have a much higher risk of experiencing hypertension and worsening of kidney disease, and their babies are at increased risk of being born premature and having low birth weight. Rates of pregnancy loss are also higher. Often women with CKD are strongly discouraged from becoming pregnant due to such risks; however, recent efforts to provide more intense care and monitoring have improved outcomes in these high-risk pregnancies.
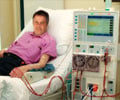
Shilpa Jesudason, MBBS, FRACP, PhD (Central and Northern Adelaide Renal and Transplantation Service, Royal Adelaide Hospital, in Australia) and her colleagues investigated the outcomes of pregnancies in women with advanced CKD who were receiving chronic dialysis treatment in Australia and New Zealand. In their study, women who conceived before starting dialysis (and then began chronic dialysis during the pregnancy) were compared with women who conceived after starting chronic dialysis.
The investigators analyzed all pregnancies reported to the Australian and New Zealand Dialysis and Transplantation Registry from 2001 to 2011, which included 77 pregnancies. Of these, 53 women conceived when they had already been established on dialysis, and 24 conceived before dialysis had commenced.
Among the major findings:• The live birth rate was 73% overall, and 82% in pregnancies that reached 20 weeks of gestation (the mid-point of pregnancy).
• Compared with women who conceived after starting dialysis, women who conceived before starting dialysis had a much better live birth rate (91% vs 63%), but their infants were of similar birth weight and gestational age. The difference in live birth rate was due to higher rates of early pregnancy loss before 20 weeks in women who conceived while established on dialysis.
• In both groups, babies were likely to be premature (median gestational age 33.8 weeks) and of low birth-weight (median birth weight 3.86 pounds), which reflects the high-risk nature of these pregnancies.
• No babies died in-utero beyond 24 weeks gestation, more than 40% of pregnancies reached beyond 34 weeks gestation (when babies' lungs can often breathe alone), extreme prematurity (born before 28 weeks) was only seen in 11.4% of pregnancies, and almost all babies survived beyond 28 days after birth.
"We can conclude that women with advanced kidney disease who start chronic dialysis after conception have superior live birth rates to those already established on dialysis at the time of conception, although these remain high-risk pregnancies," said Dr. Jesudason. She noted that for a woman with advanced CKD, putting off a pregnancy until a kidney transplant is received is ideal, but it may take years for CKD to become severe enough to require a transplant, and there may be a long wait for a suitable donor organ. Therefore, women may not be able to receive a kidney transplant until their reproductive years have passed.
Advertisement
Advertisement