Women have been oblivious of the biggest threat linked with excessive alcohol consumption-increased risk of breast cancer, according to a survey.
The YouGov survey cited that although majority of women associate liver disease or liver cancer with too much drinking, only one in five linked it to breast cancer.The results of the survey involved almost 2,000 men and women.
While there are many risk factors behind the development of breast cancer, like family history and obesity, one can easily limit the amount of alcohol consumption to keep it in check, reports BBC.
A total of 82 percent of women in the survey were not aware of the connection between alcohol and breast cancer.
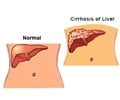
On the other hand, 95 percent linked it to liver disease, and 71 percent were aware it raised the risk of liver cancer.
The "lifetime risk" of developing breast cancer in alcohol addicts is almost one in nine.
Advertisement
Gulping down two glasses a night boosts this risk by one third, while the risk is raised to almost half on having three big glasses of wine.
Advertisement
SRM