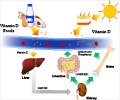
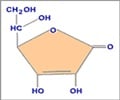
Vitamin D induces immune responses in placental tissues by stimulating production of an antimicrobial protein, a new study has shown.
The study has been published online in journal Biology of Reproduction.The study involved exposing cultured human trophoblast cells to the active form of vitamin D, leading to the production of protein cathelicidin and an increased antibacterial response in the trophoblast cells.
The team, headed by Dr. Martin Hewison, suspects that the ability of the placenta to synthesize cathelicidin varies widely among women. Their discovery suggests that placental innate immunity can be enhanced if pregnant women supplement their diets with vitamin D.
Induction of cathelicidin production by vitamin D may help the placenta stave off infection by a variety of pathogenic organisms, including staphylococcus, streptococcus, and E. coli bacteria.
Vitamin D may also enhance and sustain this bacterial killing by protecting placental trophoblast cells from infection-associated cell death.
The study presents a new mechanism for activation of innate immune responses in the placenta to protect it from infectious bacteria and sheds new light on the possible role of vitamin D in pregnancy and pregnancy-associated infection.
Advertisement
SRM