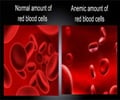
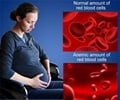
Anemia, which occurs when the body has too few oxygen-carrying red blood cells, is diagnosed and tracked by measuring hemoglobin levels. Symptoms of mild anemia include fatigue, lightheadedness and low energy. Severe and prolonged anemia can damage vital organs by depriving them of oxygen.
To examine the relationship between hemoglobin and vitamin D, the researchers looked at data from the blood samples of more than 9,400 children, 2 to 18 years of age. The lower the vitamin D levels, the lower the hemoglobin and the higher the risk for anemia, the researchers found. Children with levels below 20 nanograms per milliliter (ng/ml) of blood had a 50 percent higher risk for anemia than children with levels 20 ng/ml and above. For each 1 ng/ml increase in vitamin D, anemia risk dropped by 3 percent.
Only 1 percent of white children had anemia, compared with 9 percent of black children. Black children also had, on average, much lower vitamin D levels (18) than white children (27). Researchers have long known that anemia is more common in black children, but the reasons for this remain unclear, although some suspect that biologic and genetic factors may be at play.
The new findings, however, suggest that low vitamin D levels in black children may be an important contributor to anemia.
"The striking difference between black and white children in vitamin D levels and hemoglobin gives us an interesting clue that definitely calls for a further study," said lead investigator Meredith Atkinson, M.D., M.H.S., a pediatric nephrologist at the Johns Hopkins Children's Center.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert