New personalized treatment for bone cancer has been designed by MU veterinary oncologists to treat dogs. This treatment is different from the others- as it does not involve chemotherapy.
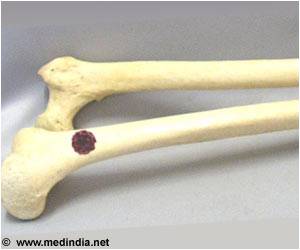
Osteosarcoma, or bone cancer, is not common in humans, representing only about 800-900 new cases each year in the U.S. About half of those cases are reported in children and teens. However, for dogs, this disease is much more common, with more than 10,000 cases a year occurring in the U.S.
"A vaccine is made out of the dog's own tumor for the dog's immune system to recognize," said Jeffrey Bryan, a professor of oncology at the MU College of Veterinary Medicine and director of Comparative Oncology Radiobiology and Epigenetics Laboratory. "The dogs received no chemotherapy and received only immunotherapy after their surgery. It's the first time that dogs with osteosarcoma have experienced prolonged survival without receiving chemotherapy, which is really exciting."
In the study, researchers partnered with ELIAS Animal Health to test a vaccine to treat osteosarcoma by using a dog's own lymphocytes. Overall, the dogs receiving this therapy had more than 400 days of remission compared to about 270 days for dogs receiving chemotherapy in a separate study by the National Cancer Institute.
"Lymphocytes are immune cells that recognize where pathogens are hiding in the body and then kill the cells harboring those pathogens," Bryan said. "After we remove the tumor, we create a vaccine using the dog's tumor cells to stimulate anti-tumor lymphocytes. These lymphocytes are then collected by apheresis and expanded outside the body by Elias Animal Health to create a transfusion of the patient's immune cells. These cells are activated and essentially really angry at whatever they are supposed to attack. When put back into the body, they should identify and destroy tumor cells. Ideally, this immune response would destroy every last tumor cell."
Mizzou researchers hope to continue immunotherapy discovery with dogs in order to optimize the new therapy for future human clinical trials with the hopes of treating osteosarcoma and other cancers, especially metastatic osteosarcoma in children.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert