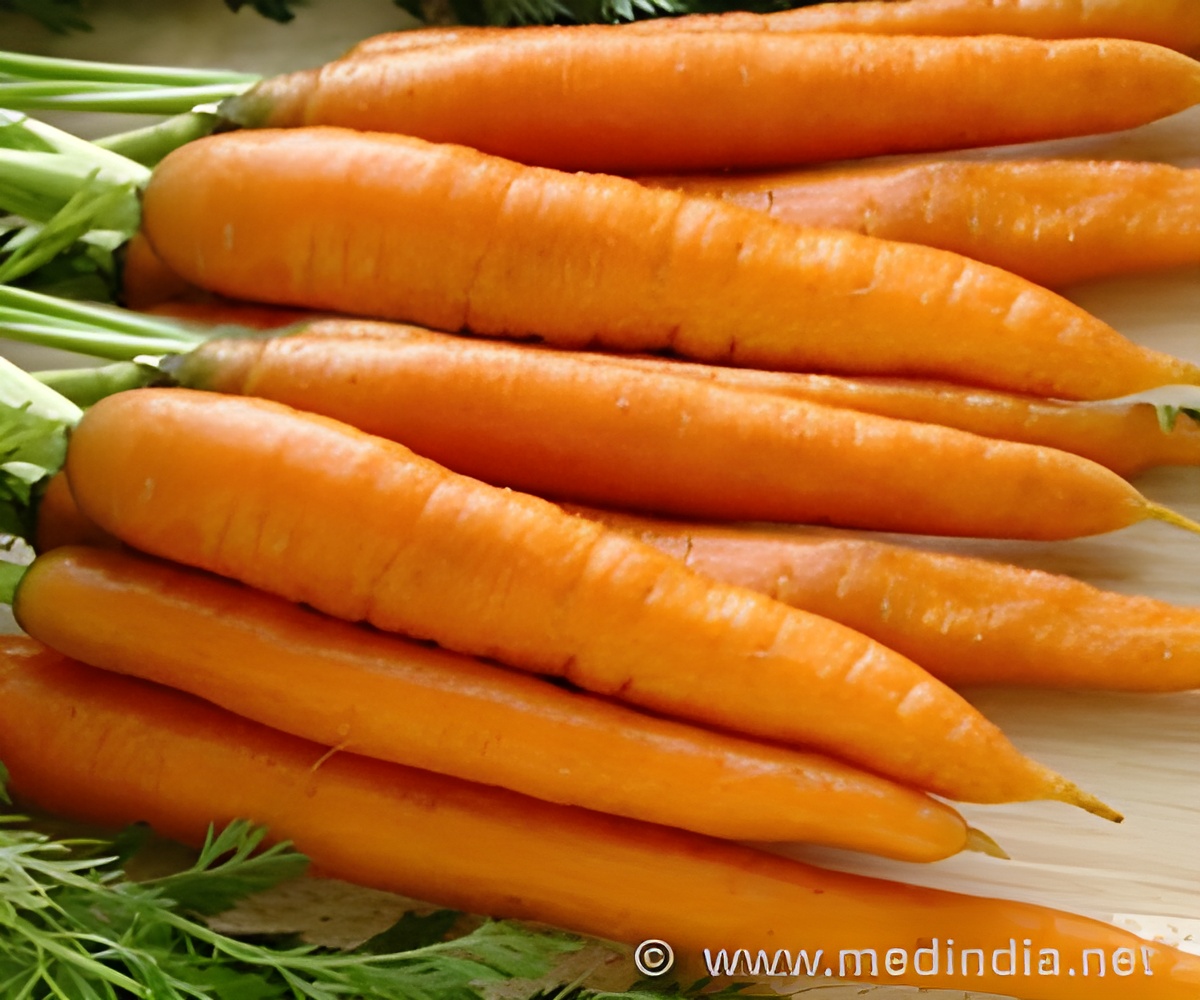
‘Carrots contain carotenoids, which is a pigment that gives distinctive orange color. Carotenoids are also antioxidants that protect against heart disease and cancer.’
Tweet it Now
"Vitamin A deficiency is a global health challenge," the study pointed out. "Its plentiful carotenoids make carrot an important source of provitamin A in the human diet."
Carotenoids were first discovered in carrots (hence the name), but which among the vegetable's newly tallied 32,115 genes was most responsible for their formation remained a mystery.
Daucus carota (the Latin name) now joins a select club of about a dozen veggies -- including the potato, cucumber, tomato and pepper -- whose complete genomes have been sequenced.
Laying bare the humble carrot's genetic secrets will make it easier to enhance disease resistence and nutritive value in other species, the researchers said.
Advertisement
"These results will facilitate biological discovery and crop improvement in carrots and other crops," said Philipp Simon, senior author and a professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Advertisement
Carrots are loaded with beta-carotene, a natural chemical that the body can transform into Vitamin A.
The deeper the orange color, the more beta-carotene.
Vitamin A is essential for normal growth and development, the proper functioning of the immune system, and vision.
Carotenoids are also antioxidants, which are thought to protect against heart disease and some forms of cancer by neutralizing so-called "free radicals", single oxygen atoms that can damage cells.
"Some of these compounds can prevent disease," Simon told AFP.
Interestingly, carrots -- along with many other plants -- have about 20 percent more genes than humans.
Looking back at the plant's family tree, scientists have been able to determine that it split with the grape about 113 million years ago and from the kiwi about 10 million years after that, when dinosaurs still lorded over the planet.
Originally white, the wild ancestors of the carrot likely came from central Asia.
Global crop production of the root has quadrupled in the last 40 years and is today eaten everywhere in the world.
There are currently no genetically modified carrots on the international market.
Source-AFP