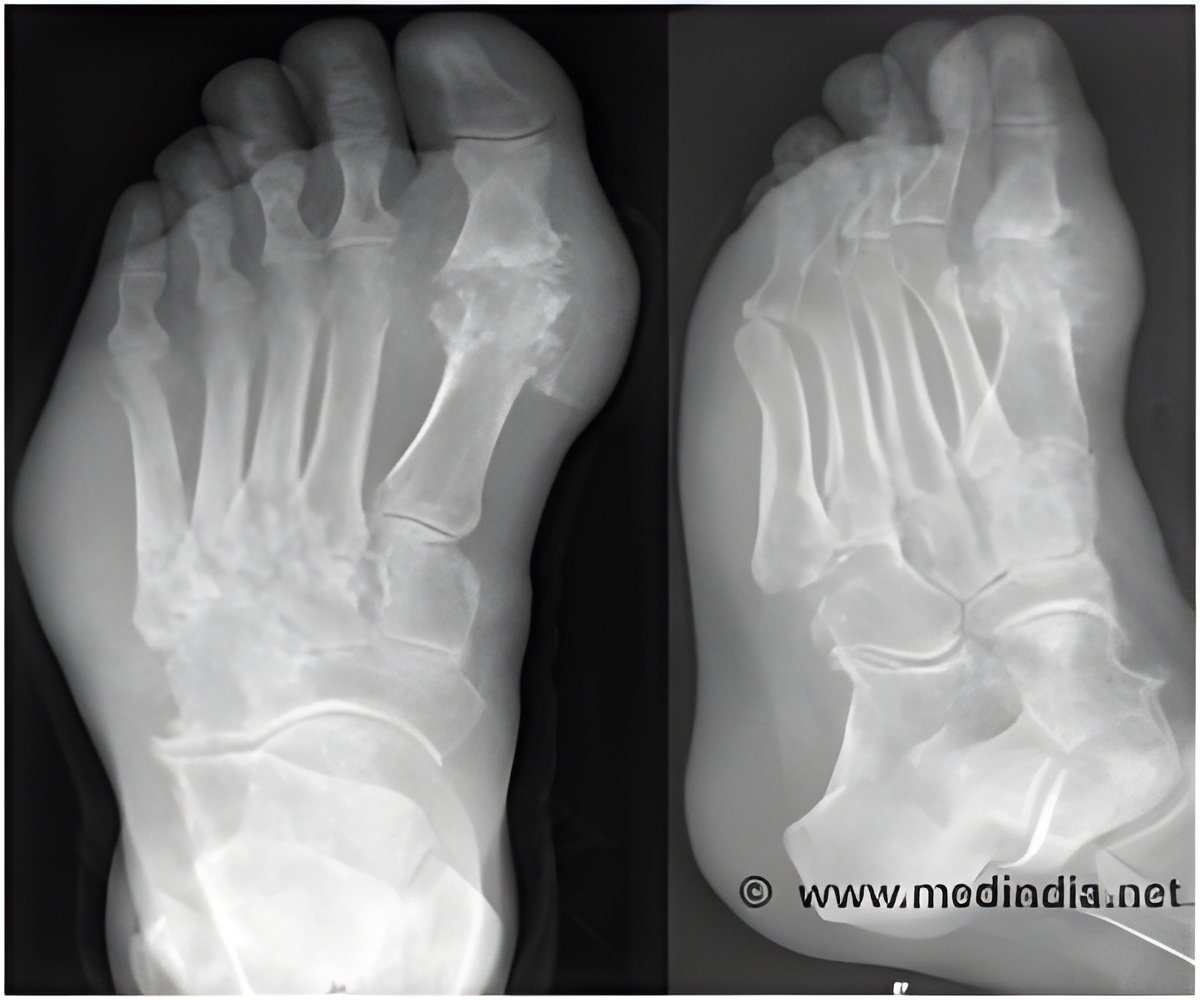
‘Hyperuricemia and gout stimulate the immune system and activate inflammatory markers which trigger renal disease.’
Tweet it Now
The common patho-physiological link appears to be the chronic, low-grade, systemic inflammation that is intrinsic to both conditions, and that may explain some of the perplexing observations noted in these clinical conditions. This thematic issue discusses the effect of the activation of the innate immune system, through stimulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to the subsequent generation of interleukins and the release of cytokines and chemokines, and how these factors interact in the complex interplay between hyperuricemia, gout and kidney disease.
Source-Eurekalert