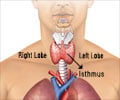
The number of thyroid operations being done in elderly patients is on the rise due to an increasing geriatric population, a steady increase in thyroid cancer incidence over the last 20 years and a higher rate of benign thyroid pathology in the elderly. In the current study, researchers wanted to know if age had an effect on postoperative risks in thyroidectomy patients and found that elderly patients were at increased risk for major systemic complications.
"As the baby-boomer generation ages, the U.S. population is becoming increasingly older, and because of this, more research with a focus on elderly patients needs to be a study priority," said Raymon H. Grogan, MD, of the University of Chicago in Illinois, and lead author of the study. "Our findings demonstrate this need by showing how conventional wisdom in the medical setting does not always apply to the elderly population."
This is one of the largest studies ever performed that looks specifically at thyroid surgery and elderly patients. In this study, researchers examined 7,915 thyroidectomy patients from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database and noted outcome measures such as urinary tract infection, cardiac complications, total hospital length of stay and 30-day mortality. They found that when compared to younger patients, elderly patients (age 65-79) are twice as likely and the super-elderly (age 80 and above) are five times as likely to have a postoperative complication.
"It is important to understand that our study emphasizes the importance of the entire medical system that cares for these elderly patients, not just the surgeon," says Grogan. "In our study elderly patients were susceptible to life-threatening, non-surgical complications. Thus it is important that an elderly patient undergoing thyroid surgery have an experienced team of primary care physicians, surgeons, anesthesiologists and nurses who handle these types of surgeries on a routine, daily basis."
Source-Newswise