"This study goes beyond previous associations of vitamin D with various health outcomes. It outlines a clear chain of cellular events, from the binding of DNA, through a specific signaling pathway, to the reduction of proteins known to trigger inflammation," said study lead author Elena Goleva, assistant professor of pediatrics at National Jewish Health.
"Patients with chronic inflammatory diseases, such as asthma, arthritis and prostate cancer, who are vitamin D deficient, may benefit from vitamin D supplementation to get their serum vitamin D levels above 30 nanograms/millilitre," she said.
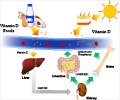
Researchers examined the specific mechanisms by which vitamin D might act on immune and inflammatory pathways. They incubated human white blood cells with varying levels of vitamin D, then exposed them to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a molecule associated with bacterial cell walls that is known to promote intense inflammatory responses.
Cells incubated with no vitamin D and in solution containing 15 ng/ml of vitamin D produced high levels of cytokines IL-6 and TNF-alpha, major actors in the inflammatory response. Cells incubated in 30 ng/ml vitamin D and above showed significantly reduced response to the LPS. The highest levels of inflammatory inhibition occurred at 50 ng/ml.
Through a complex series of experiments, the researchers identified a new location where the vitamin-D receptor appears to bind directly to DNA and activate a gene known as MKP-1. MKP-1 interferes with the inflammatory cascade triggered by LPS, which includes a molecule known as p38, and results in higher levels of IL-6 and TNF-alpha.
Advertisement
Source-ANI