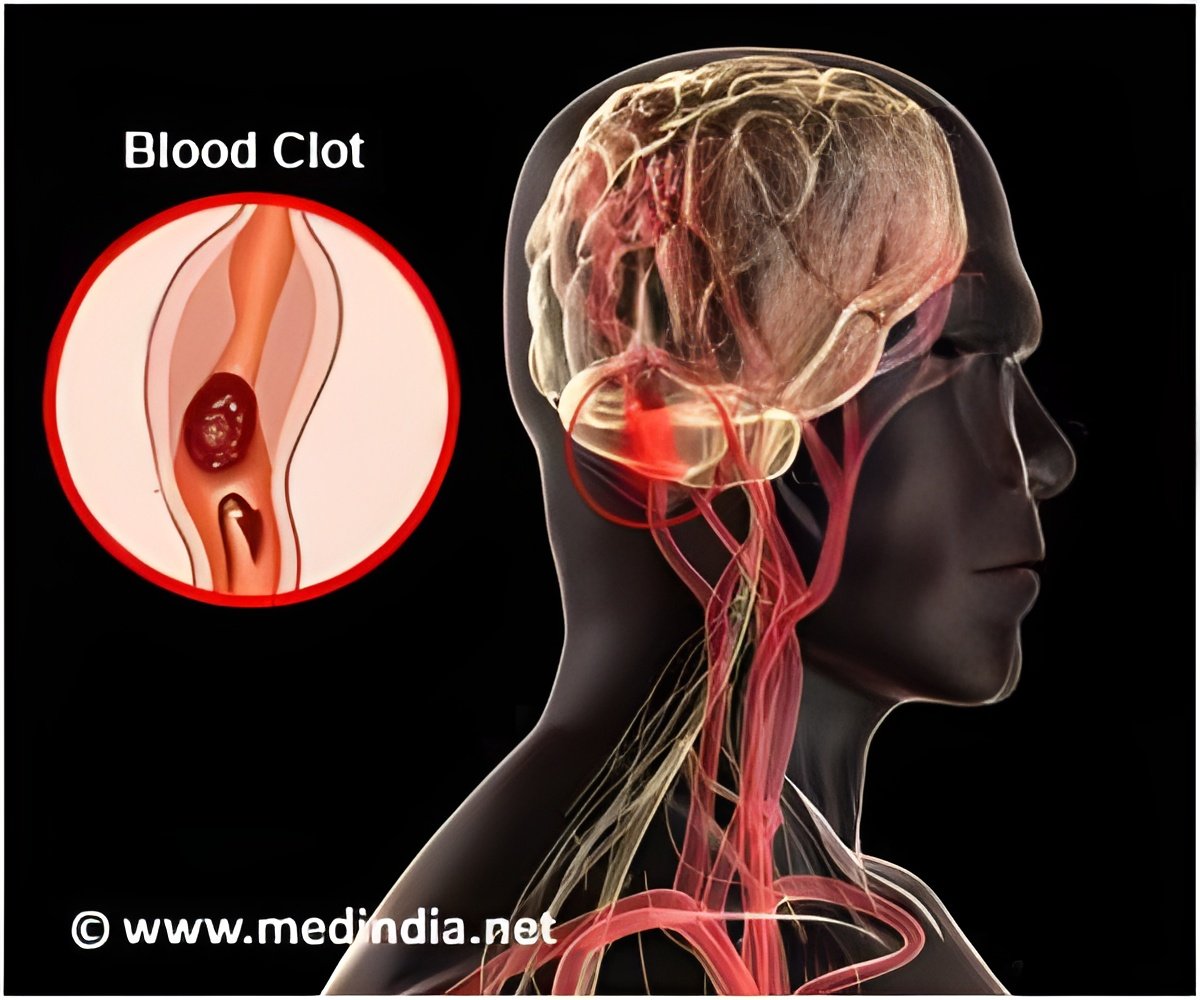
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures or is blocked by a blood clot. Stroke victims are usually given intravenous tissue plasminogen activator (IV tPA) that works by dissolving the clot and improving blood flow to the part of the brain being deprived of blood flow. Surgical approach involves a minimally invasive procedure called thrombectomy to remove the clot. The neurovascular surgeon threads a catheter through an incision in the patient’s groin, snaking it through the blood vessels and into the brain. He then uses a device attached to the catheter to grab and dislodge the clot and pull it all the way out through the incision. A new study has found that surgical removal of the blood clot plus standard medication yields better long term outcomes in patients with severe stroke than drug alone.
Co-author Demetrius Lopes from Rush University Medical Center said, "These findings are a game-changer for how they should treat certain types of stroke and these outcomes are the difference between patients being able to care for themselves after stroke and being dependent."
The study found that the patients who received IV tPA plus thrombectomy exhibited reduced disability across the entire range of the measurement, with a functional independence rate of 60% compared to 35.5% for those patients who received only IV tPA. The study revealed that for every 2.6 patients treated, one additional patient had an improved disability outcome; for every four patients treated, one additional patient was independent at 90 day follow-up. The study also found that patients who received thrombectomy had better cerebral blood flow rates at 27 hours after treatment, with 82.8% of those patients who had blood flow that was 90% of normal or better, versus 40.4% of patients who only received IV tPA.
The study is published in the
New England Journal of Medicine.Source-Medindia