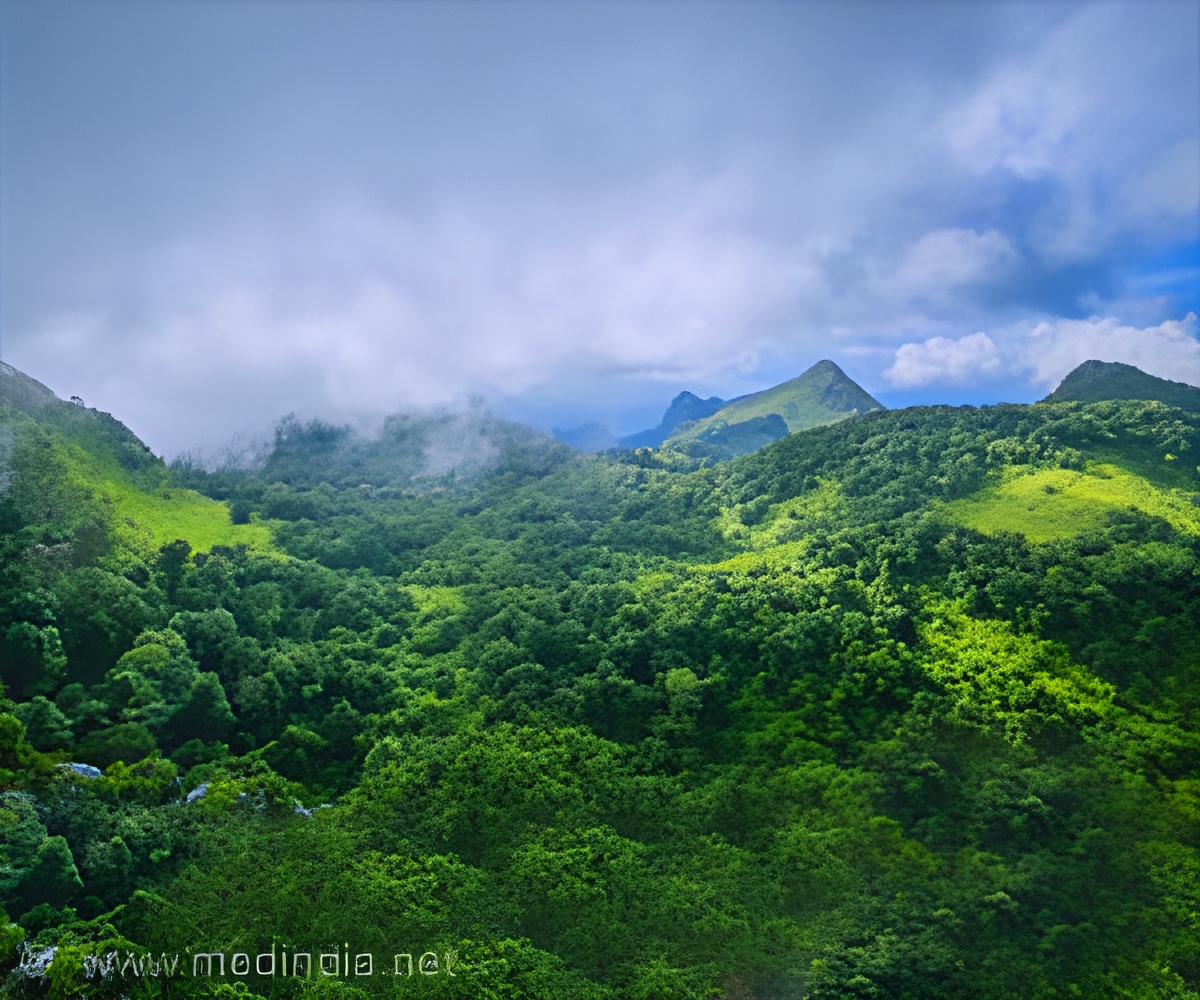
"Some temperate forests already appear to be showing chronic effects of warming temperatures, such as slow increases in tree deaths," said study co-author Nathan Stephenson, ecologist with the US Geological Survey.
"But the emergence of megadisturbances, forest diebacks beyond the range of what we have normally seen over the last century, could be a game-changer for how we plan for the future," Stephenson noted.
Many forests are remarkably resilient, re-growing after years of logging.
Yet, reviewing enormous body of work on the subject, the researchers found that climate change and rising global temperatures are giving rise to "hotter" droughts -- droughts that exhibit a level of severity beyond that witnessed in the past century.
During a hotter drought, high air temperatures overheat leaves and also increase the stress on trees by drawing the moisture from their tissues at faster rates than normal.
Advertisement
And as temperatures rise in many regions, fires grow in frequency and severity causing losses in private property, natural resources and lives, the study said.
Advertisement
The study was published in the journal Science.
Source-IANS