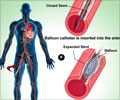
The nanoparticles, which acts as antioxidants can be triggered using, directed infrared light, flow and temperature sensors for physiological sensing, and an array for data storage.
The feasibility and safety of the stents using a canine model has been tested but some of the components used in the stent would have to go through regulatory approval before its use in humans. The team now plans to focus on developing a method to incorporate wireless batteries and data communication into the stent design.
Source-Medindia