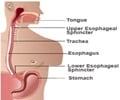
Researchers at Duke University Medical Center claim to have identified how GERD, or gastroesophageal reflux disease, drives the development of asthma.
Dr. Shu Lin, an assistant professor of surgery and immunology at Duke, conducted experiments with mice and discovered that inhaling tiny amounts of stomach fluid that back up into the esophagus, a hallmark of GERD, produces changes in the immune system that trigger asthma.In the study, researchers inserted miniscule amounts of gastric fluid into the lungs of mice (mimicking the human process of micro-aspiration, or breathing in tiny amounts) over a period of eight weeks.
They compared these animals'' immune systems with those of mice that were exposed to allergens but not the gastric fluid.
Researchers noted that the immune systems of the two sets of mice responded very differently.
Those that had the gastric fluid in their lungs developed what researchers call a T-helper type 2 response, a type of immune system reaction characteristic of asthma.
The other mice responded in a more balanced manner, mounting an immune reaction consisting of both T-helper type 1 and T-helper type 2 responses.
Advertisement
"These data suggest that chronic micro-aspiration of gastric fluid can drive the immune system toward an asthmatic response," Lin added.
Advertisement
"But it may mean that people with GERD may be more likely to develop asthma. If there is an upside to this, it is that developing GERD is something we can pretty much treat and control," he added.
The study is published online in the European Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Source-ANI
SRM