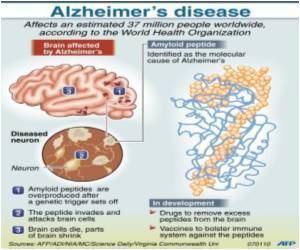
The APOE gene, which comes in several different forms, is related to increased risk of developing Alzheimer's disease.
People with APOE e4/e4 gene type have the highest risk of developing the disease and people with APOE e3/e3 have a neutral risk.
Discovering the important mechanisms underlying how APOE e4/e4 increases Alzheimer's risk has been one of the most vexing mysteries facing Alzheimer's researchers for over a decade.
Luminescent conjugated oligothiophenes (LCOs) or luminescent conjugated polymers (LCPs), the newly discovered class of biomarkers, can stick to protein structures in the body and emit colors reflecting the different shapes or forms of the proteins.
Among other uses, LCPs/LCOs are currently being employed in test tubes, animal models, and autopsied Alzheimer's brains to study the structure of proteins deposits caused by the disease.
Advertisement
In the study, frozen brain sections from people who died with Alzheimer's were stained using two LCPs/LCOs: pentamer formyl thiophene acetic acid (pFTAA) and polythiophene acetic acid (PTAA).
Advertisement
Using pFTAA revealed that tau tangle densities in e4/e4 Alzheimer patients that were apparently greater than those with e3/e3.
"The findings support our hypothesis that APOE genotype changes amyloid structure. This is important because the different shapes might respond differently to treatments that attempt to clear amyloid deposits from the brain. We already know, for example, that APOE e4/e4 patients respond less well to anti-amyloid antibody with bapineuzumab," said Gandy.
The study was presented at the 2010 Alzheimer's Association International Conference on Alzheimer's Disease in Honolulu, Hawaii. (ANI)
Source-ANI