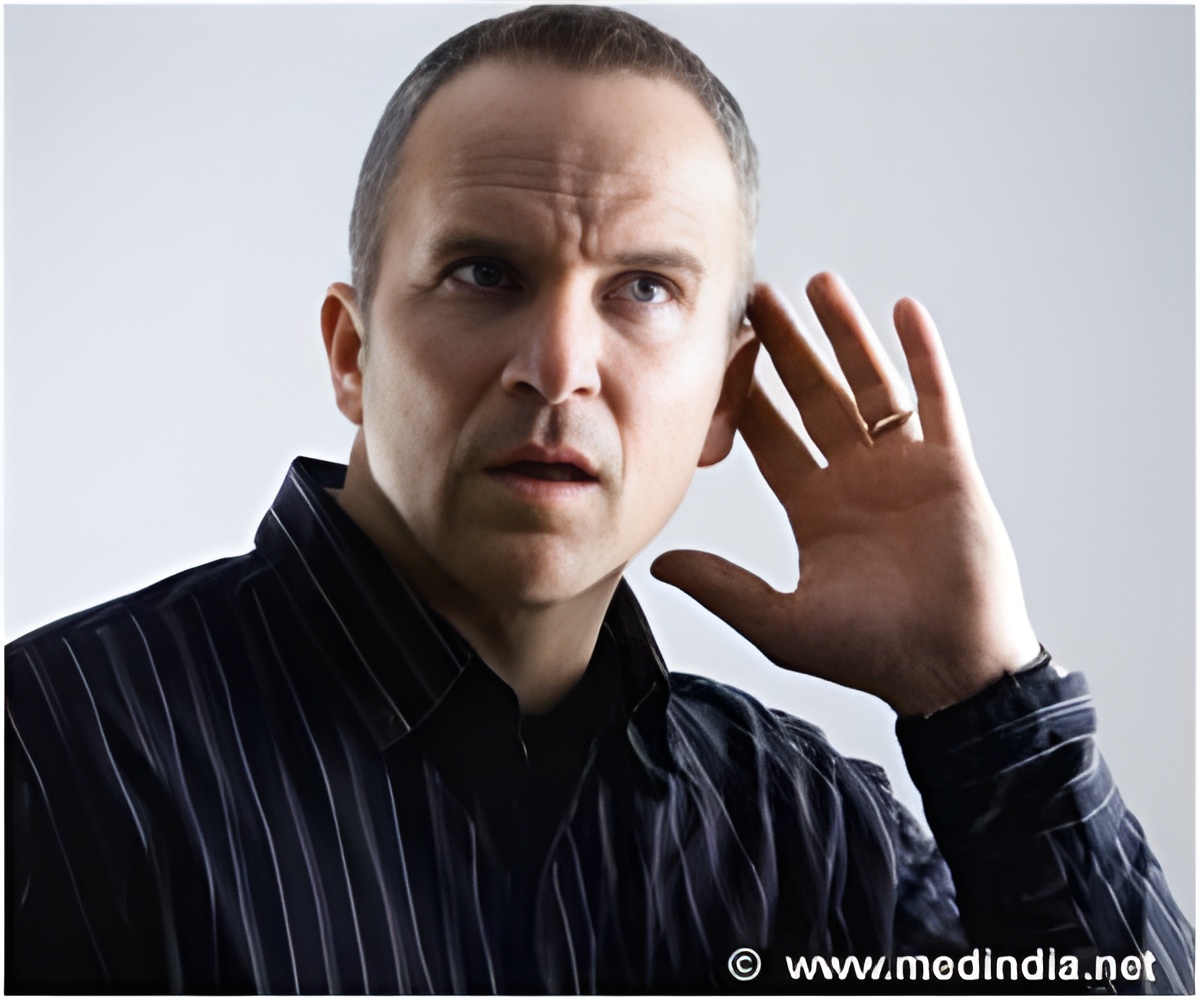
Timbre is a hard-to-quantify concept loosely defined as everything in music that isn't duration, loudness or pitch. For instance, timbre comes into play when we are able to instantly decide whether a sound is coming from a violin or a piano.
Mounya Elhilali and colleagues from Johns Hopkins University set out to develop a mathematical model that would simulate how the brain works when it receives auditory signals, how it looks for specific features and whether something is there that allows the brain to discern these different qualities.
The authors devised a computer model to accurately mimic how specific brain regions transform sounds into the nerve impulses that allow us to recognize the type of sounds we are listening to.
The model was able to correctly identify which instrument was playing (out of a total of 13 instruments) to an accuracy rate of 98.7 percent.
The model mirrored how human listeners make judgment calls regarding timbre. The researchers asked 20 people to listen to two sounds played by different musical instruments. The listeners were then asked to rate how similar the sounds seemed.
Advertisement
"There is much to be learned from how the human brain processes complex information such as musical timbre and translating this knowledge into improved computer systems and hearing technologies," Elhilali said.
Advertisement
Source-ANI