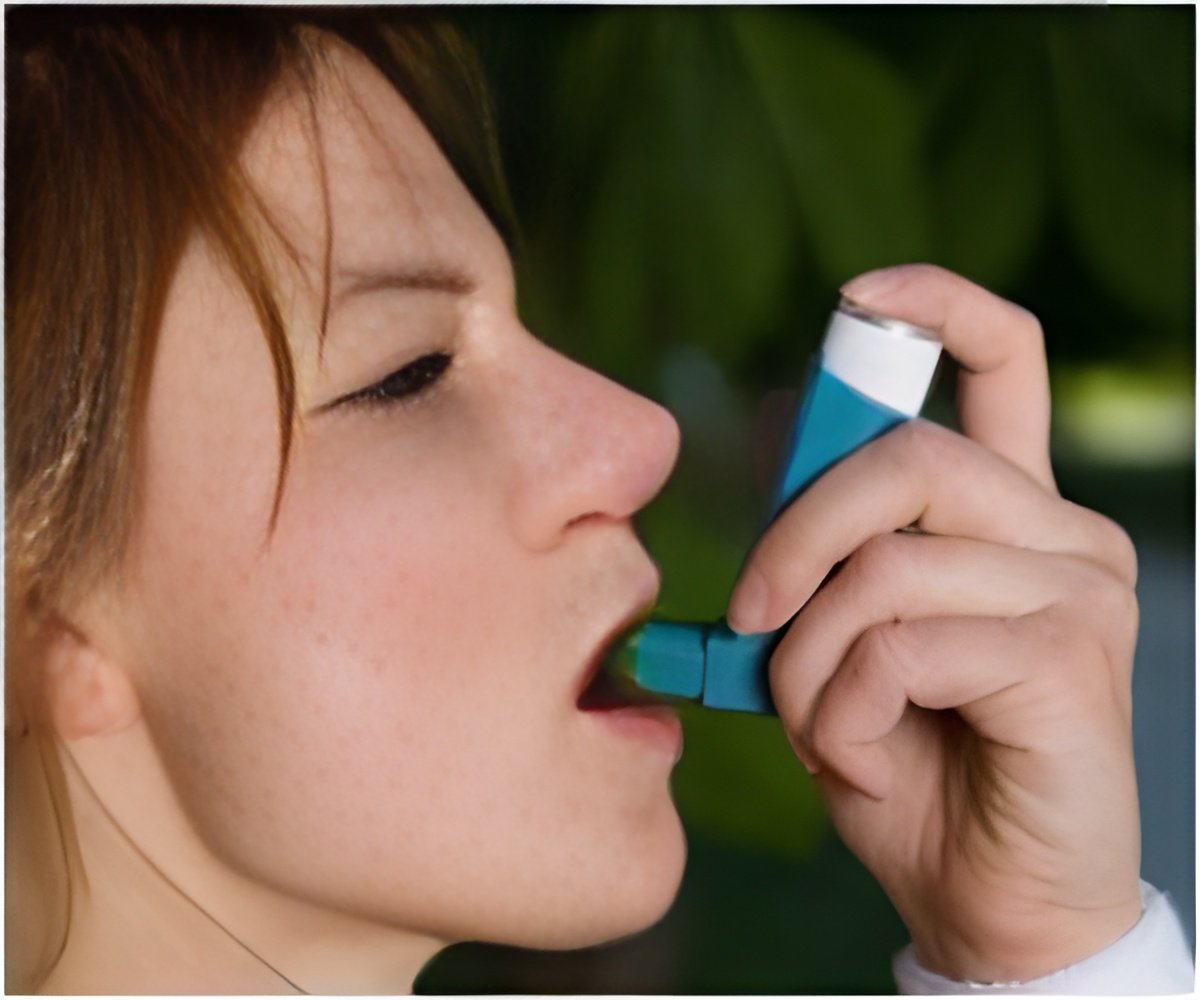
Patients often poorly take their medication based on the onset and degree of symptoms.
Henry Ford researchers have said that this is the first time that asthma medication use has been tracked closely over time and related to the likelihood of severe asthma attacks.
"Our findings demonstrated a relationship between medication adherence and asthma events in a manner that accounts for the changing patterns of inhaler use over time," says lead author Keoki Williams, M.D., MPH, an Internal Medicine physician and associate director of Henry Ford's Center for Health Policy and Health Service Research.
Inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) medication is the most effective treatment for controlling symptoms and preventing attacks, which can lead to a visit to the emergency department or hospitalization or death if left untreated.
Working from their theory that ICS use changes with the episodic nature of asthma, Dr. Williams and his team of researchers measured changes in medication use over time and to estimate the effect of ICS use on asthma attacks among 298 patients. Patients were followed on average for two years and had 435 asthma attacks during that time.
Advertisement
"But most importantly, we found that causal use of these medications is not enough, especially among patients whose asthma is not controlled. Patients must use their asthma controller medication as prescribed if they want to have the best chance of preventing serious asthma attacks."
Advertisement
Source-ANI