Early immune intervention at a young age treat the eczema and prevent other allergic diseases which usually follow the development of atopic dermatitis.
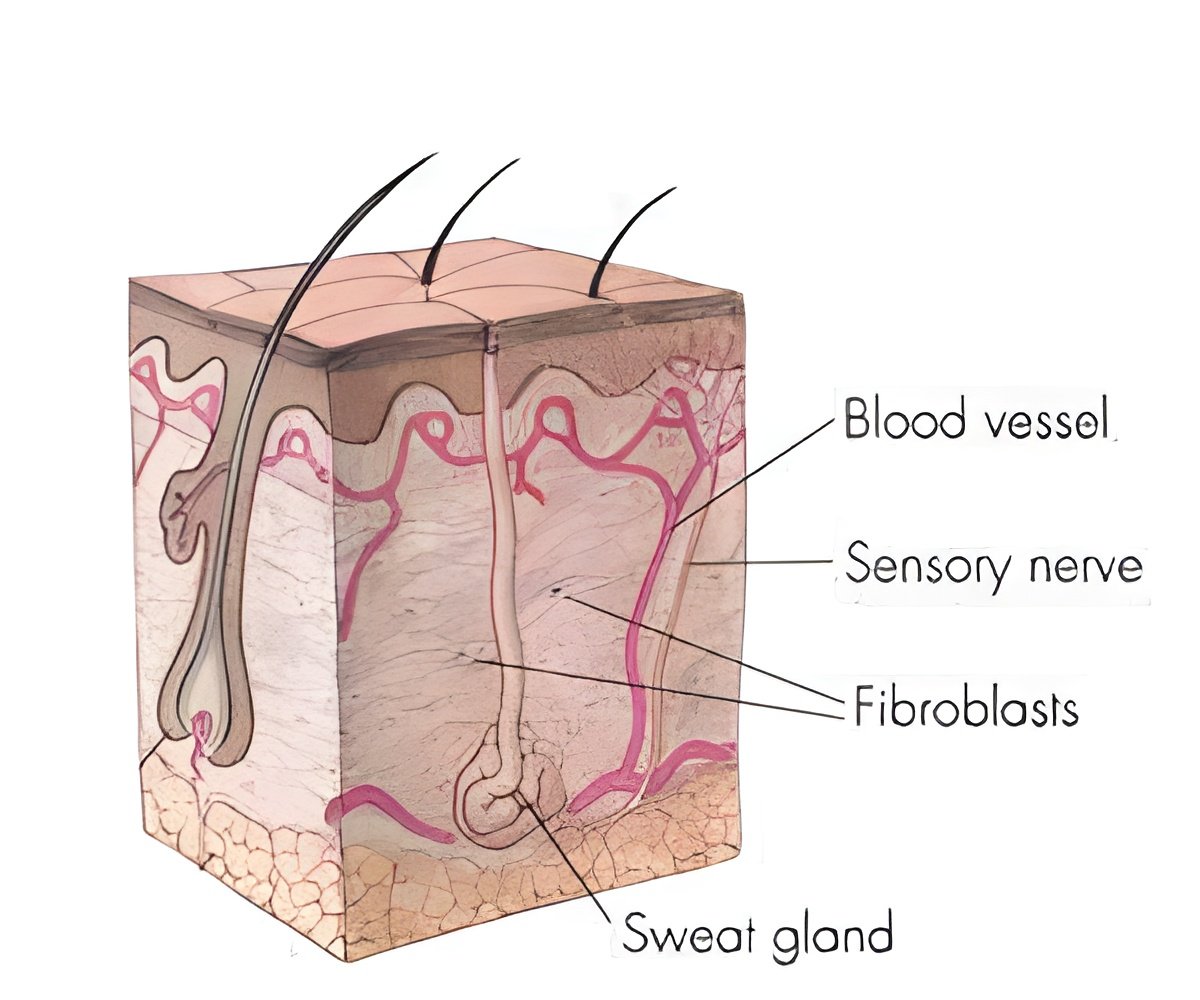
‘The pediatric atopic dermatitis profile has robust and significant increases of Th17 T lymphocyte cells, which are characteristically increased in psoriasis.’





The researchers found that the non-lesional, or normal-appearing, skin of young children with early eczema is already highly abnormal with significant immune activation, simulating that of lesional skin of adults with many years of active disease.“The important findings may suggest the need for early immune intervention at a young age, not only to treat the eczema but perhaps also to prevent other allergic diseases such as asthma, food allergies, seasonal allergies which usually follow the development of research on AD focuses on the mechanism of the underlying disease and promotes development of targeted therapeutics. Her past research has identified biomarkers for current treatments for AD.
The study also highlighted some important differences between the adult and pediatric phenotypes. First, the research showed that pediatric AD is associated with increased lymphocyte activation, including Th2 lymphocyte cells, which is also similar to adults with AD.
Next, the researchers discovered that that unlike the adult disease, the pediatric eczema profile has robust and significant increases of Th17 T lymphocyte cells, which are characteristically increased in psoriasis, a disease that is now being successfully targeted in using anti IL-17 and IL-23-targeting strategies.
“In addition to targeting Th2 lymphocyte cells as in adults, treatment approaches for children with eczema may need to target other types of T lymphocytes, particularly Th17 T lymphocytes,” said Dr. Guttman-Yassky.
Advertisement
Atopic dermatitis is an inflammatory, extremely itchy skin disorder that affects 10 to 20 percent of children in the United States and more than 31 million adults. According to Dr. Paller, understanding the similarities and differences between eczema in pediatric patients versus adult patients is important for making treatment decisions for children. “For the first time, this study shows that many of the same changes seen in adult AD are, in fact, present and sometimes even greater in infants and young children with moderate to severe AD within 6 months of disease onset,” said Dr. Paller.
Advertisement
The study is published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Source-Newswise