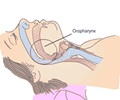
Being stressed and fatigued may be the way of life for patients who suffer from both allergic rhinitis and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA).
In a paper presented at the 2009 American Academy of Otolaryngology – Head and Neck Surgery Foundation (AAO-HNSF) Annual Meeting & OTO EXPO in San Diego, researchers studied 34 people who were diagnosed with obstructive sleep apnea. Among them, 12 people were classified in the allergic rhinitis group and 22 people in the control group. The researchers evaluated BMI (Body Mass Index), AHI (Apnea Hypopnea Index), RERA (Respiratory effort related arousals), LSAT (Lowest O2 Saturation), RQLQ (Rhinoconjunctivitis Quality of Life Questionnaire), ESS (Epworth sleepiness scale), stress score, fatigue score, and ability to cope, with questionnaires of both groups, then statistically compared mean scores of both groups.Allergic rhinitis is well known for increasing patients' daytime somnolence, fatigue, and decreasing cognitive performance, as does OSA. But there have not been previous studies that showed the result if both diseases coexist.
Mean fatigue scores were 38.8 and 29.9 each, which were significantly higher in the allergic rhinitis group. That group showed higher stress scores, decreased ability to cope, and higher mean ESS, but they were not significant.
The authors note that their findings should highlight that patients who have both allergic rhinitis and obstructive sleep apnea might need more careful management and multiple therapeutic options to help relieve their symptoms. Additionally, patients with either allergic rhinitis or OSA should also be evaluated for the other condition to ensure appropriate care.
Source-Eurekalert
RAS