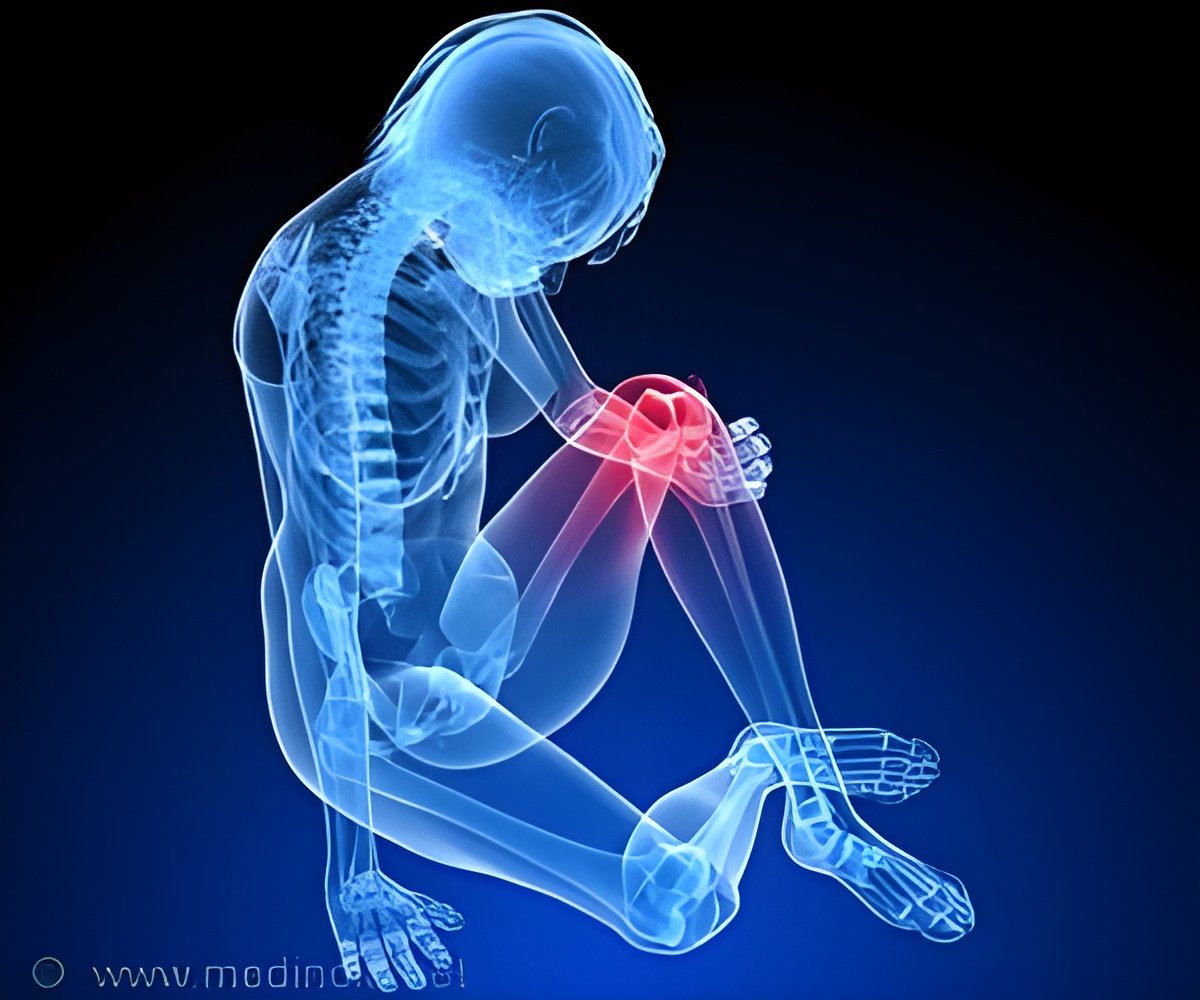
Using a patient classification system, a new report has found that more than one-third of the total knee replacement surgeries in the US could be classified as inappropriate. The study, published in
Arthritis & Rheumatology, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), highlights the need for consensus on patient selection criteria among U.S. medical professionals treating those with the potential need of knee replacement surgery.
The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality reports more than 600,000 knee replacements are performed in the U.S. each year. In the past 15 years, the use of total knee arthroplasty has grown significantly, with studies showing an annual volume increase of 162% in Medicare-covered knee replacement surgeries between 1991 and 2010. Some experts believe the growth is due to use of an effective procedure, while others contend there is over-use of the surgery that relies on subjective criteria.
The present study led by Dr. Daniel Riddle from the Department of Physical Therapy at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond, examined the criteria used to determine the appropriateness of total knee arthroplasties. "To my knowledge, ours is the first U.S. study to compare validated appropriateness criteria with actual cases of knee replacement surgery," said Dr. Riddle.
Source-Eurekalert