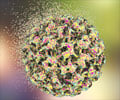
‘New skin cell culture technique sheds light on important genetic information about early stages of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.’
Tweet it Now
HPV infects skin cells known as keratinocytes before they have fully matured, or differentiated, and are still dividing into new cells. During the final stages of differentiation, uninfected cells cease division, but HPV makes infected cells keep dividing, the researchers said. For the study, published in the journal PLOS, the research team took inspiration from recent reports that, before entering a keratinocyte, HPV16 binds to the extra cellular matrix -- a mesh of proteins and carbohydrates outside of the cell that performs a variety of structural and molecular functions.
They found that high infection rates could be achieved by incubating HPV16 with extra cellular matrix materials in a dish, and then seeding it with keratinocytes.
They analysed RNA from infected cells at different time points to determine which HPV genes were expressed and when.
They also infected cells with mutant HPV16 viruses lacking different genes, revealing which viral proteins were essential to establish infection.
Advertisement
Source-IANS