‘The newly developed fibrinogen nanofibers hold great potential for various biomedical applications in the future.’
Tweet it Now
Because of its versatile molecular interactions, fibrinogen is often processed into hydrogels and fibrous scaffolds for cell culture and tissue engineering applications in vitro. However, existing ways of doing this - such as electrospinning or the preparation of fibrin hydrogels - use organic solvents, high electric fields or enzymatic activity, which change the molecular structures or native protein functions of fibrinogen. To solve this, the team wanted to find out if they could develop a simple and well-controllable way to make three-dimensional scaffolds while retaining fibrinogen's properties.
Professor Brüggemann said: "For the first time, we were able to assemble fibrinogen into dense, three-dimensional scaffolds without using high voltages, organic solvents or enzymatic activity. Our biofabrication process can be controlled simply by adjusting the fibrinogen and salt concentration, and the pH range."
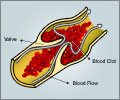
The dimensions of the scaffolds reached diameters in the centimeter range and a thickness of several micrometers. With 100 to 300 nm, the diameters of self-assembled fibres were in the range of native ECM fibers and fibrin fibers in blood clots. Professor Brüggemann added: "This novel class of fibrinogen nanofibers holds great potential for various biomedical applications. For example, in future studies on blood coagulation our immobilized fibrinogen nanofibers could provide a valuable in vitro platform for initial drug screening. On novel wound healing applications, it will be highly interesting to study the interaction of fibroblasts and keratinocytes with our free-standing fibrinogen scaffolds."
Advertisement