‘Nicotine and caffeine are some of the most commonly used and highly addictive substances in modern society, but they are often overlooked as a potential source of significant withdrawal symptoms when abruptly discontinued in ICU.’
Tweet it Now
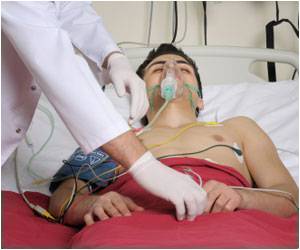
"Withdrawal symptoms including nausea, vomiting, headaches, and delirium can last for up to 2 weeks. These symptoms resemble conditions such as meningitis, encephalitis, and intracranial haemorrhage--this may confuse clinical diagnosis and result in unnecessary tests which can cause patient harm, cost a lot of money, and waste time." In Europe, up to 27% of the population smokes, and more than half drink coffee. The systematic review, synthesising all the available evidence from the scientific literature, included 12 studies investigating withdrawal symptoms and treatment in ICUs between 2000 and 2018, involving 483 adults (aged 18-93).
Results showed that acute nicotine withdrawal substantially increases agitation (64% smokers vs 32% non-smokers) and the number of tracheal tube and intravenous line displacements caused by agitation in ICU patients (14% smokers vs 3% non-smokers).
However, nicotine substitution therapy was shown to contribute to the development of ICU delirium (severe confusion and disorientation)--which is associated with prolonged intubation, increased length of stay, and greater risk of dying.
Abrupt caffeine withdrawal leads to drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, headaches, and can increase rates of ICU delirium. Caffeine benzoate has been successfully used to treat headaches but substitution in the ICU has a limited evidence base.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert