A non-invasive treatment, that has been tested on in the UK, may provide the much – required relief to Type 1 diabetes patients who need a daily jab.
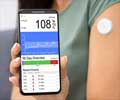
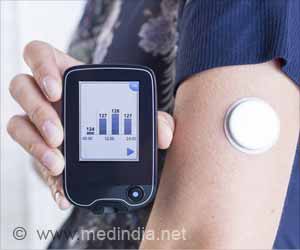
The treatment, an insulin pump, works by mimicking the body’s pancreas delivering measured doses of insulin through the layer of tissue just beneath the skin.It completely rules out the use of injections.
The results have impressed the patients who reportedly admitted an improved quality of life.
A consultant at the Royal Cornwall Hospital in Truro, Dr Duncan Brown, also revealed that the insulin pump could also prevent hypoglycaemic attacks.
He said that the 'unpredictable attacks' of diabetes can hamper the routine life of patients and the pump can reverse it for them.
"For some patients with Type 1 this can be very disabling," the BBC quoted him, as saying.
Advertisement
"The pump can reverse this, meaning they have a better quality of life and can get back to doing normal things like driving."
Advertisement
MAR/P