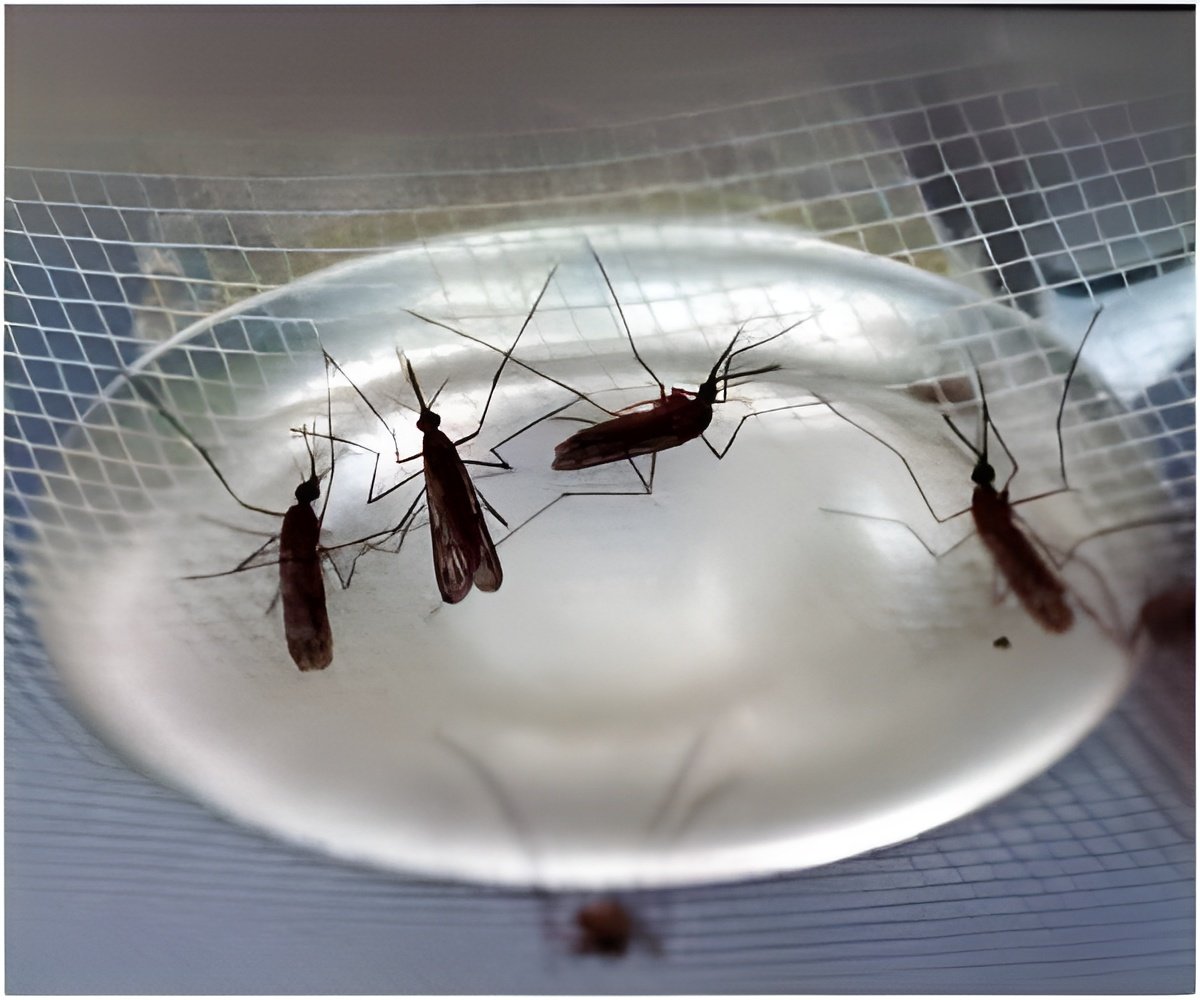
Two especially prolific vectors are the yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti) and Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus), which is easy to spot because of its striped patterning. Although native to Africa and Asia, these insects can spread through the western world by hitching rides in used tires, which trap water to create a perfect breeding site.
Kevin Myles and Zach Adelman, both associate professors of entomology in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, lead the research, which is published in the Jan . 5 PLoS Pathogens article, "Production of Virus-Derived Ping-Pong-Dependent piRNA-like Small RNAs in the Mosquito Soma," by Elaine M. Morazzani and Michael R. Wiley, Ph.D. students in entomology; Marta G. Murreddu, research associate in entomology; and Adelman; and Myles.
"We have previously shown that an antiviral response directed by small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) is present in culicine mosquito vectors. However, we show here that another class of virus-derived small RNAS, exhibiting many similarities with ping-pong-dependent piwi-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) is also produced in the soma of culicine mosquitoes," the authors explain. Myles, Adelman, and co-workers made use of a technique called next generation sequencing to aid in their discovery.
The newly discovered antiviral pathway appears to act redundantly to the previously described small interfering RNA (siRNA) pathway, indicating a robust immune system, said Myles. Thus, understanding how viruses get around the mosquito's dual antiviral responses poses an increasingly interesting challenge to scientists.
"In the case of mosquito-borne pathogens, our health depends as much on the mosquito's immune response as it does on our own immune response, yet surprisingly little is known about the immune system of the mosquito," Myles said.
Advertisement