‘The drug, rimegepant, is awaiting U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval and may offer advantages over currently available migraine medications.’
Tweet it Now
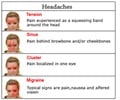
Debilitating Disorder Migraine headache affects about 12 to 14% of people, or more than a billion individuals worldwide. This chronic neurologic disorder involves periodic attacks of head pain along with symptoms that may include nausea as well as sensitivity to light and sound. More than three-quarters of migraine sufferers experience at least one migraine attack per month, and more than half are severely impaired during their attacks.
Currently, many people with migraine take triptan drugs (examples include sumitriptan, eletriptan, and rizatriptan), which were introduced in the 1990s. Triptans halt acute migraines by stimulating serotonin receptors, which in turn reduces inflammation and constricts blood vessels. But triptans don't help everyone, they can produce intolerable side effects, and--since they constrict vessels--shouldn't be taken by people with cardiovascular disease (CVD) or major CVD risk factors.
New Mechanism for Relief
People not helped by triptans, or those who can't take them, may benefit from the new class of drugs called, gepants, which includes rimegepant. Gepants work by targeting the receptors for a small protein, called CGRP, long implicated in migraine. During migraine attacks, CGRP is released resulting in pain. Gepants relieve the pain and other symptoms of migraine by blocking the CGRP pathway.
Advertisement
Two hours after taking their tablets, 19.6% of patients in the rimegepant group were free from pain compared with 12.0% in the placebo group--a statistically significant difference. Freedom from their most bothersome symptoms occurred in 37.6% of patients in the rimegepant group and 25.2% in the placebo group. Side effects were minimal, with nausea and urinary tract infections the only adverse effects reported in more than 1% of patients in each group and no adverse CVD effects observed.
Advertisement
Source-Eurekalert