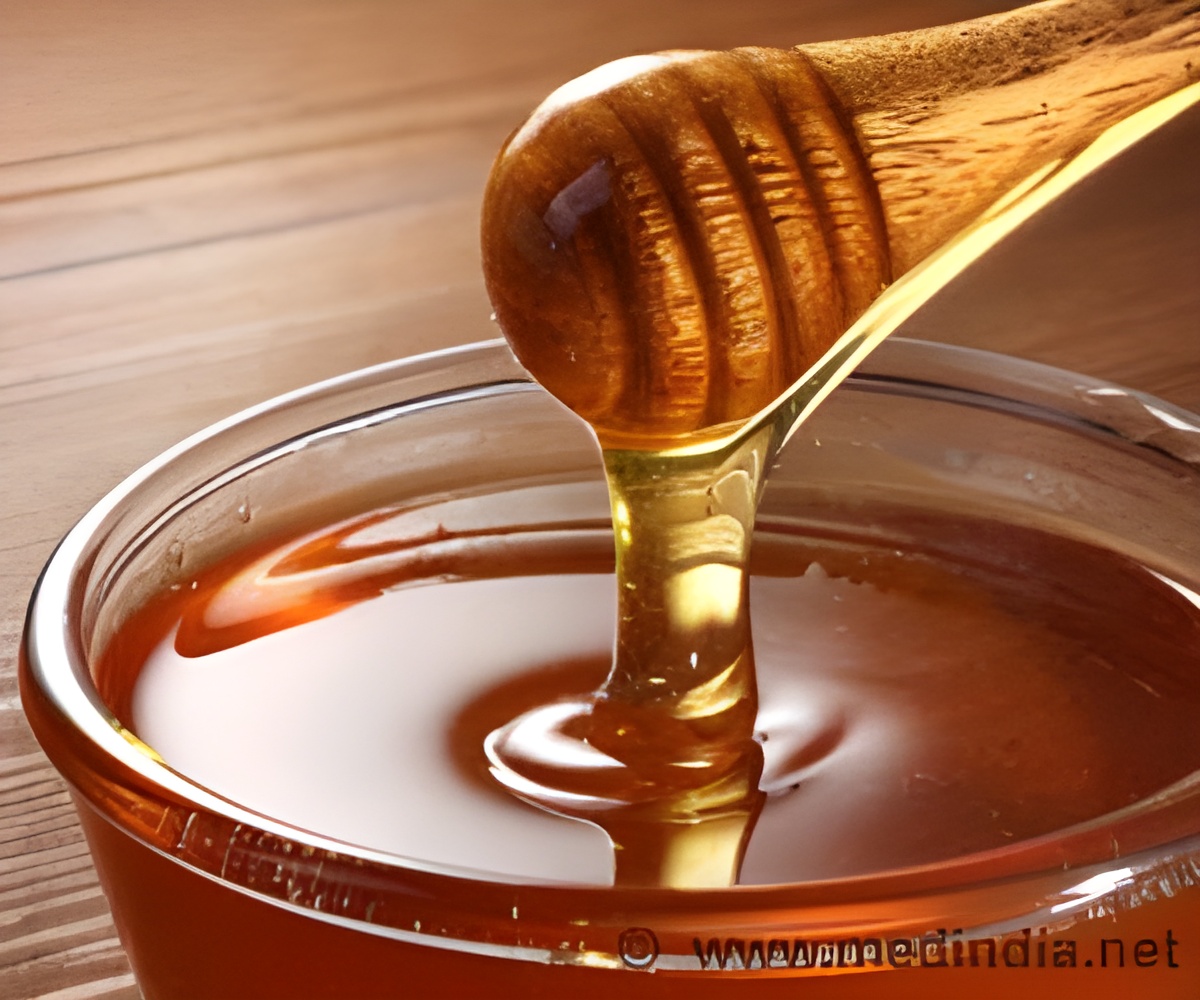
‘Combining a natural ingredient such as manuka honey with amikacin drugs used for killing bacteria will treat resistant lung infections completely.’
Tweet it Now
Now scientists have found that manuka honey has the potential to kill several drug-resistant bacterial infections such as Mycobacterium abscessus, which usually affects patients with cystic fibrosis (CF) or bronchiectasis.Cystic fibrosis is a genetic condition affecting around 10,800 people - one in every 2,500 babies born in the UK -and there are more than 100,000 people with the condition worldwide. In this long-term condition, the airways of the lungs become widened causing a build-up of excess mucus that can make the lungs more vulnerable to infection.
Mix of Traditional and Modern Medicine for Treating Deadly Lung Infection
In the study, the researchers used samples of the bacteria Mycobacterium abscessus taken from 16 infected CF patients. They then tested the antibiotic amikacin, combined with manuka honey, to discover what dosage was required to kill the bacteria.As part of the study, the team used a lab-based lung model and nebulizer - a device that produces a fine spray of liquid often used for inhaling a medicinal drug.
By nebulizing manuka honey and amikacin together, it was found they could improve bacterial clearance, even when using lower doses of amikacin, which would result in fewer life-changing side effects for the patient.
This new approach is advantageous not only because it has the potential to kill off a highly drug-resistant infection, but because of the reduced side effects, benefitting quality of life and greatly improving survival chances for infected CF patients.
Advertisement
But the researchers found that the new combination using manuka honey, required a dosage of just 2 micrograms per milliliter of amikacin - resulting in a one-eighth reduction in the dosage of the drug.
Advertisement
However, the use of this potential treatment combining amikacin and manuka honey shows great promise as an improved therapy for these terrible pulmonary infections.
Source-Medindia