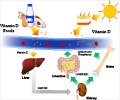
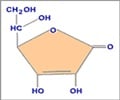
Lack of vitamin D, which is absorbed primarily through exposure to sunlight, may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD), according to a new study.
A growing body of evidence links low 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels to common CVD risk factors such as hypertension, obesity and diabetes, as well as major cardiovascular events including stroke and congestive heart failure.The study has been published in the December, 9, 2008, issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
"Vitamin D deficiency is an unrecognized, emerging cardiovascular risk factor, which should be screened for and treated," said James H. O'Keefe, M.D., cardiologist and director of Preventive Cardiology at the Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, MO.
"Vitamin D is easy to assess, and supplementation is simple, safe and inexpensive," the expert added.
Low vitamin D levels activate the renin-angiostensin-aldosterone system and, in doing so, predispose patients to hypertension and a stiffening and thickening of the heart and blood vessels. Vitamin D deficiency also alters hormone levels and immune function, which can increase the risk of diabetes, a major contributor to CVD.
Vitamin D can also be consumed through supplements and food intake. Natural food sources of vitamin D include salmon, sardines, cod liver oil, and vitamin D-fortified foods including milk and some cereals.
Advertisement
Source-ANI
SPH