Researchers have discovered a molecule could be a likely key driver in identifying the development and progression of colorectal cancer and could be an important target as well. The study of microRNA-135b (miR-135b) in two animal models and human tumors was published in the journal
Cancer Cell and was led by researchers at The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) and at the University of Glasgow in the United Kingdom.
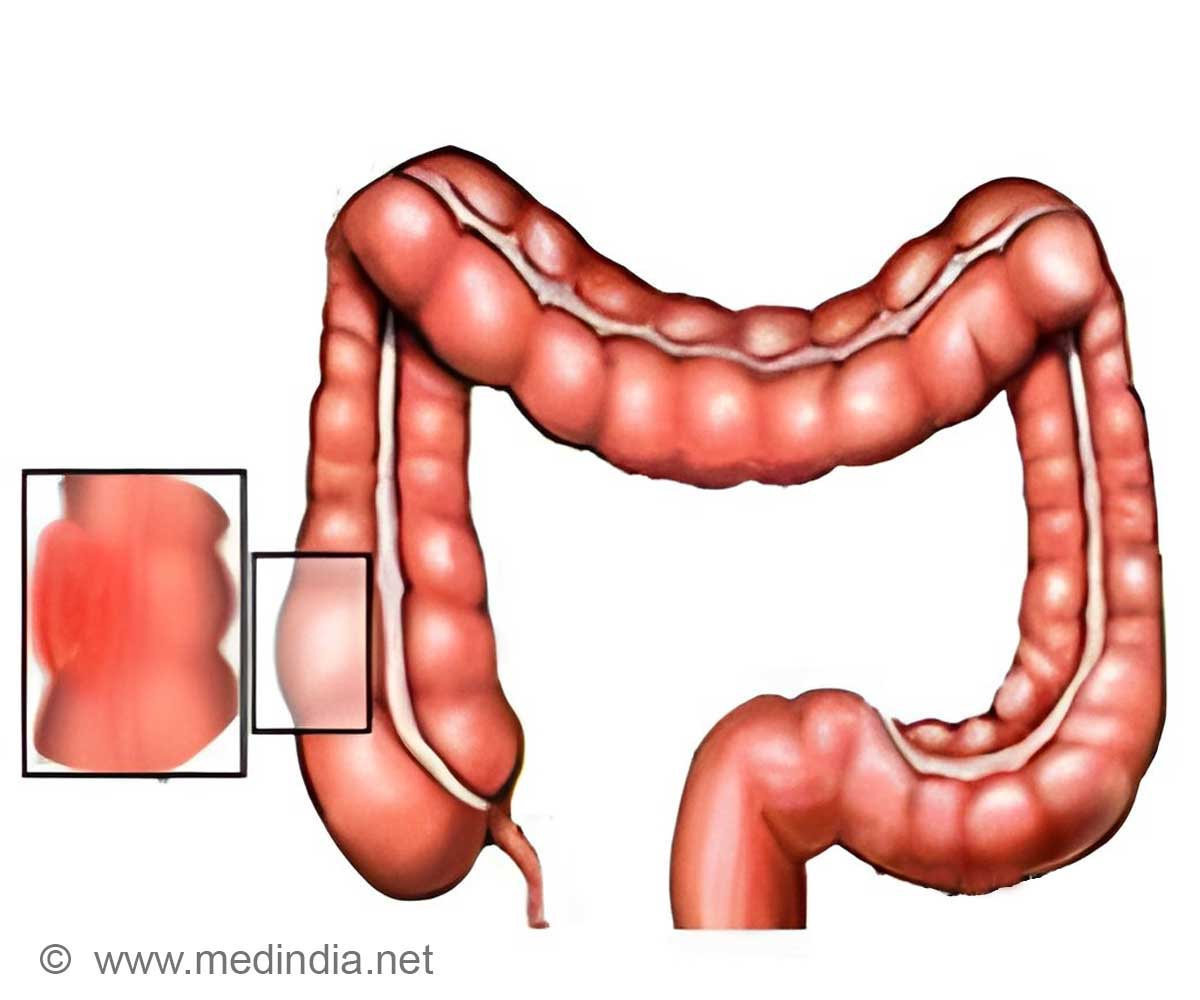
The researchers demonstrate that miR-135b is present at abnormally high levels in both mouse and human colorectal (CRC) tumors. The overexpression can be induced by the mutations in either well-known oncogenes or tumor-suppressor genes that frequently occur in CRC, the researchers say."We found that miR-135b is up-regulated in both sporadic and inflammatory bowel disease-associated colorectal cancer, and that its up-regulation is associated with tumor stage and poor clinical outcome," says principal investigator Carlo M. Croce, MD, chair of molecular virology, immunology and medical genetics, and director of Human Cancer Genetics at Ohio State and the OSUCCC – James."
Our findings provide proof-of-principle that anti-miR-135b has significant therapeutic potential in colorectal cancer treatment," says Croce, who is also the John W. Wolfe Chair in Human Cancer Genetics. For this study, Croce and his collaborators used a CRC mouse model based on loss of a tumor suppressor and a model based on inflammation and oncogene activation; human tumors from a cohort of sporadic CRC and inflammatory-bowel-disease associated CRC; human and animal cell lines and data from The Cancer Genome Atlas.
Key findings included:- MiR-135b up-regulation occurs in both sporadic and inflammatory bowel disease-associated CRC, and it is associated with tumor stage and poor clinical outcome;
- Loss of the APC gene, deregulation of the PTEN/PI3K pathway and over-expression of the SRC oncogene all trigger miR-135b over-expression;
- Artificial miR-135b over-expression increases cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis, as occurs with APC loss or PI3K or SRC activation.
- Delivering anti-miR-135b in an inflammation-related CRC mouse model affected proliferation and apoptosis, resulting in reduced tumor number and size.
Source-Eurekalert