‘The immune clock could be valuable for people at risk of cardiovascular events and also for immune-compromised patients susceptible to infection.’
Tweet it Now
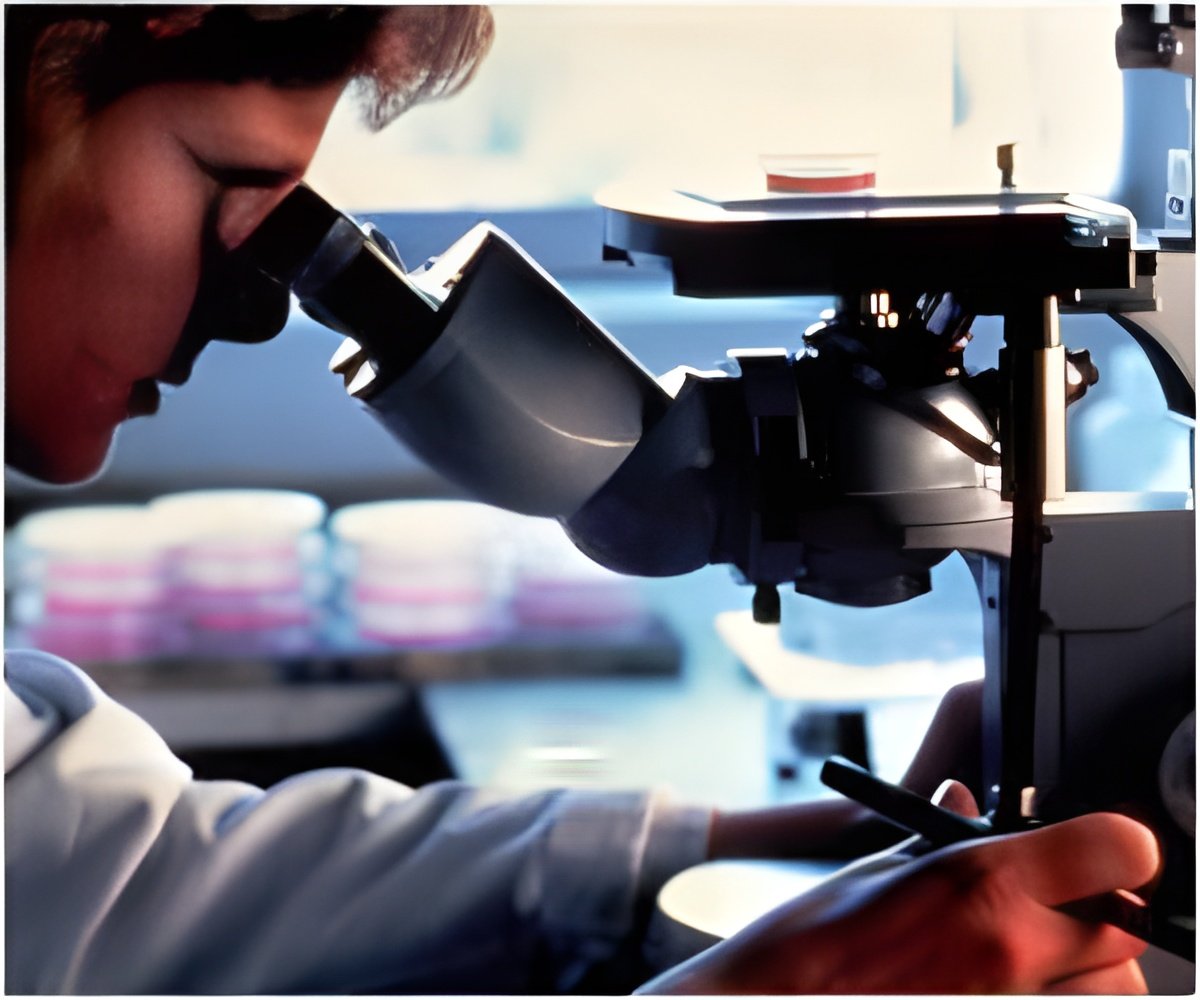
Human beings generally hold the conceited view that ours is the dominant species, but the true masters of the living world are the billions upon billions of microorganisms--including bacteria, fungi, and viruses. These microorganisms occupy every environment, including our bodies, and are essential for all other life on the planet. We thus have no choice but to accept their presence, but this cohabitation breaks down when some of these microorganisms enter our bloodstream and organs, becoming pathogens that cause disease and death.The immune system, especially through the action of neutrophils, ensures peaceful coexistence with microorganisms by efficiently eliminating those that cause infection. Nevertheless, this comes at a price, because the immune response is often disproportionate and damages healthy tissue. According to Andrés Hidalgo, "this is what happens, for example, during myocardial infarction, stroke, and acute lung injury. The biological challenge is to control the immune system so that it protects against infection but does not cause collateral damage to the body." The new study by Hidalgo's group, published in Immunity, presents a response to this challenge that could have important repercussions for health care.
The research team combined genetic techniques with high-resolution microscopy imaging in live mice to track the behavior of neutrophils over the course of the day. Using animal models of myocardial infarction, stroke, and infection, the team demonstrated that the immune response behaved very differently at different times of day. In the words of study author Alejandra Aroca "by specifically manipulating this genetic clock, we were able to make animals highly resistant to infection, but these same animals were extremely vulnerable to infarction." The study also shows evidence that this immune clock exists in humans.
These findings are important because this type of cardiovascular injury is responsible for most deaths in advanced economies, and a large majority of these clinical events occur in the early morning; in other words, they follow a circadian pattern. Given the overlapping circadian patterns of cardiovascular disease, infection, and immunity, the research team examined the possibility of a causal relationship. "We observed that if we eliminated the clock in the neutrophils of mice, the circadian patterns in infection and infarction disappeared," explained Adrover. Thus, "during the day, the neutrophils caused more damage in an infarction, but at the same time became more efficient at eliminating pathogens. If we can learn to control this immune clock, we can take advantage of this association to improve treatments for patients."
Due to the worldwide high prevalence of infectious and cardiovascular diseases, the study could have wide ranging clinical implications. The team is currently working on ways to manipulate this immune clock with drugs to induce diurnal or nocturnal immunity, depending on the needs of each patient.
Advertisement