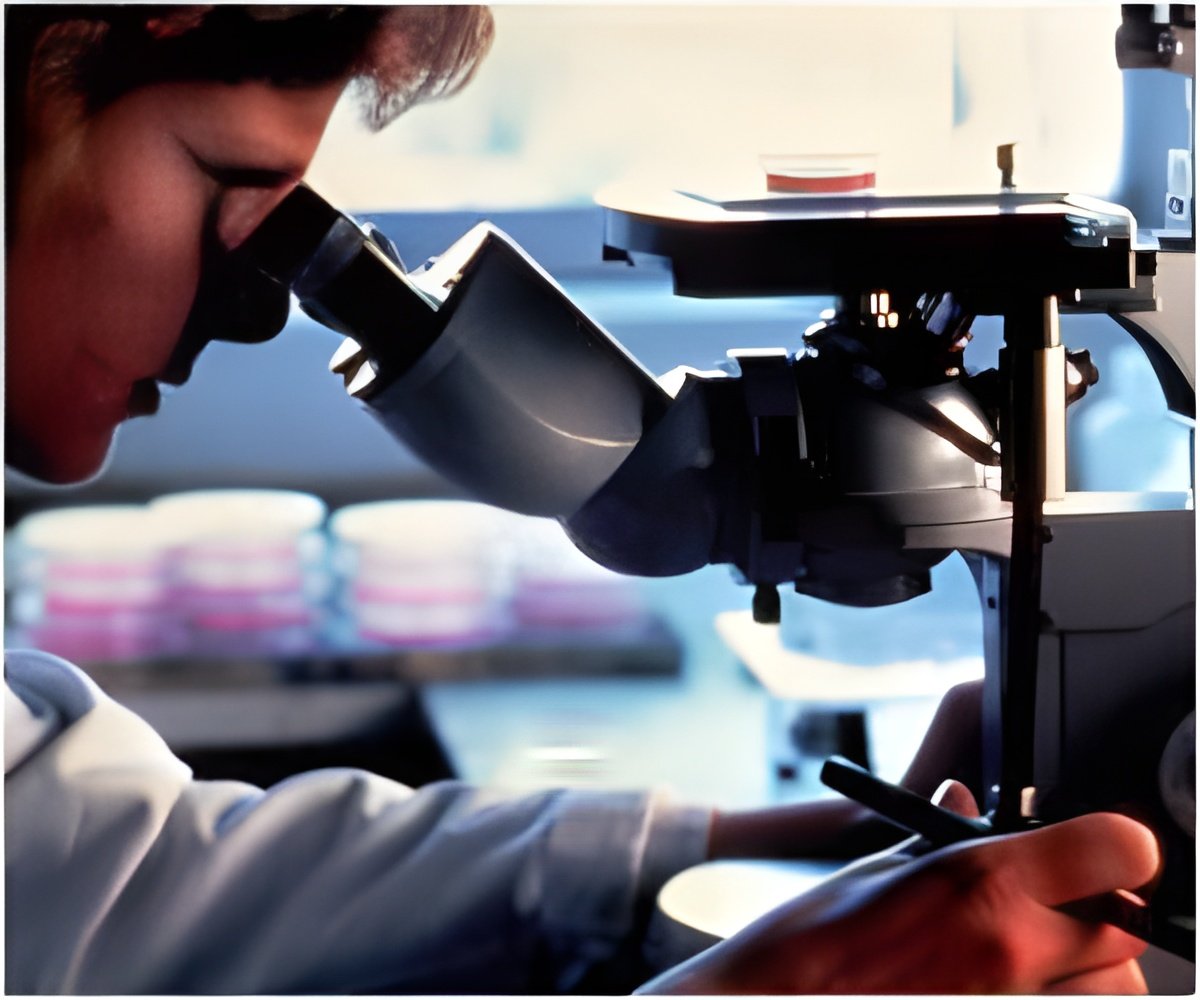
‘Hepatitis E virus-like particles could be used as vaccines or anti-cancer drugs that are delivered through food or drink. The idea is that you would drink the vaccine, and after passing through the stomach the virus-like particles would get absorbed in the intestine and deliver it to the target organ.’
Tweet it Now
Such particles could be used as vaccines that are delivered through food or drink. The idea is that you would drink the vaccine, and after passing through the stomach the virus-like particles would get absorbed in the intestine and deliver vaccines to the body. But the particles could also be used to attack cancer. Stark and Cheng did some tinkering with the proteins, so that they carry sticky cysteine amino acids on the outside. They could then chemically link other molecules to these cysteine groups.
They worked with a molecule called LXY-30, developed by researchers at the UC Davis Comprehensive Cancer Center, which is known to stick to breast cancer cells. By using a fluorescent marker, they could show that virus-like particles carrying LXY-30 could home in on breast cancer cells both in a laboratory dish and in a mouse model of breast cancer.
Results of the study are published in Nanomedicine. So perhaps one day, cancer patients might drink their medicine and UC Davis-designed virus-like particles carrying anticancer drugs will home in on their target.
Source-Eurekalert