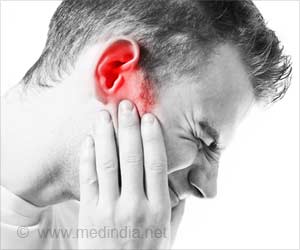
Discover the world of tinnitus - a phantom ringing in the ears. Uncover the causes, symptoms, and dangers associated with this common condition.
- Tinnitus is the perception of sound in the ears when there is no external noise and can manifest as ringing, buzzing, or humming
- While tinnitus is often harmless, it can be a symptom of underlying health issues such as hearing loss, ear infections, or vascular problems
- Seeking medical attention for persistent or severe tinnitus is crucial to identify potential causes and ensure proper management to prevent potential complications
Tinnitus: Diagnosis and Management
Go to source) . It is commonly described as ringing, buzzing, hissing, or humming in the ears, but the sound experienced can vary from person to person. Tinnitus can be classified into two types: subjective and objective.
Subjective Tinnitus - Heard Only by the Affected Individual
Subjective tinnitus is the most prevalent form of tinnitus, characterized by sounds that are perceived only by the person experiencing it. This type of tinnitus is commonly associated with damage to the auditory system caused by various factors, such as exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or age-related hearing loss.Objective Tinnitus - Audible During Medical Examination
Objective tinnitus, in contrast, is much rarer than subjective tinnitus and differs in that the sound can be heard by both the affected individual and a healthcare professional during a medical examination. This type of tinnitus is typically linked to underlying vascular issues or muscle contractions near the ear.Tinnitus as a Signal of Underlying Health Issues
In many cases, tinnitus is a benign condition that does not indicate a serious health problem. It can be triggered by temporary factors like excessive noise exposure, stress, caffeine, or certain medications. However, in some instances, tinnitus can be a signal of an underlying health issue that demands prompt attention.Hearing Loss:
Tinnitus is often associated with hearing loss, which can be caused by age, exposure to loud noises, or certain medical conditions. Sensorineural hearing loss, resulting from damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve, is a common culprit behind tinnitus.Ear Infections:
Infections in the middle or inner ear can cause tinnitus due to inflammation and fluid buildup, impacting the proper functioning of the auditory system.Meniere's Disease:
This inner ear disorder can lead to tinnitus, along with vertigo (dizziness) and hearing loss (2✔ ✔Trusted SourceTinnitus and underlying brain mechanisms
Go to source) .
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorders:
Problems with the TMJ, which connects the jaw to the skull, can cause tinnitus in some cases.Ototoxic Medications:
Certain medications, such as certain antibiotics, diuretics, and chemotherapy drugs, can have a side effect of causing tinnitus.Head or Neck Injuries:
Trauma to the head or neck can damage the auditory system and lead to tinnitus.Vascular Issues:
Conditions that affect blood flow, like high blood pressure or atherosclerosis, can cause objective tinnitus by generating turbulent blood flow near the ears.Tumor:
Although rare, a benign tumor called an acoustic neuroma can develop on the cranial nerve responsible for hearing, leading to tinnitus and other symptoms.When To Seek Medical Attention for Tinnitus
If you experience tinnitus, particularly if it is persistent, severe, or accompanied by other concerning symptoms, it's essential to seek medical advice promptly. While most cases of tinnitus are not life-threatening, identifying and addressing the underlying cause early on can prevent potential complications and ensure proper management.Consult an Audiologist:
If you notice persistent ringing in your ears or a decline in your hearing ability, schedule an appointment with an audiologist. They can perform hearing tests and assess the extent of the issue.Visit an Ear, Nose, and Throat (ENT) Specialist:
If tinnitus is interfering with your daily life or accompanied by vertigo, dizziness, or ear pain, an ENT specialist can conduct a thorough examination to identify potential causes and recommend appropriate treatments.Manage Stress:
Stress and anxiety can exacerbate tinnitus. Consider stress-relieving techniques such as meditation, yoga, or counseling to cope better with the condition (3✔ ✔Trusted SourceTinnitus: The Sound of Stress?
Go to source) .
Protect Your Ears:
If you work in a noisy environment or enjoy loud recreational activities, use ear protection to prevent potential damage to your hearing.Unexplained ringing in the ears, or tinnitus, can be a distressing and persistent condition that affects millions worldwide. While it is often benign and temporary, it can sometimes be a signal of an underlying health issue that requires attention. By understanding the potential causes and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can effectively manage tinnitus and address any potential dangers associated with it. Remember to prioritize your hearing health, and don't hesitate to seek professional assistance to ensure a better quality of life.
References:
- Tinnitus: Diagnosis and Management - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34060792/)
- Tinnitus and underlying brain mechanisms - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22931904/)
- Tinnitus: The Sound of Stress? - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6407646/)